Atropine
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Atropen, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682487 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
by mouth, IV, IM, rectal |
| Drug class | antimuscarinic (anticholinergic) |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 25% |
| Metabolism | ≥50% hydrolysed to tropine and tropic acid |
| Onset of action | ~ 1 minute |
| Biological half-life | 2 hours |
| Duration of action | 30 to 60 min |
| Excretion | 15–50% excreted unchanged in urine |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| Synonyms | Daturin |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.096 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
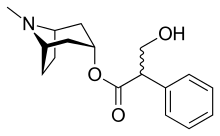
| Formula | C17H23NO3 |
| Molar mass | 289.369 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Atropine is a medication used to treat certain types of nerve agent and pesticide poisonings, some types of slow heart rate, and to decrease saliva production during surgery. It is typically given intravenously or by injection into a muscle. Eye drops are also available which are used to treat uveitis and early amblyopia. The intravenous solution usually begins working within a minute and lasts half an hour to an hour. Large doses may be required to treat some poisonings.
Common side effects include a dry mouth, large pupils, urinary retention, constipation, and a fast heart rate. It should generally not be used in people with angle closure glaucoma. While there is no evidence that its use during pregnancy causes birth defects, it has not been well studied. It is likely safe during breastfeeding. It is an antimuscarinic (also known as an anticholinergic) that works by inhibiting the parasympathetic nervous system.
Atropine occurs naturally in a number of plants of the nightshade family including deadly nightshade, Jimson weed, and mandrake. It was first isolated in 1833. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system. It is available as a generic medication and is not very expensive. A one-milligram vial costs between US$0.06 and US$0.44, wholesale, in the developing world.
...
Wikipedia
