Hexachloroantimonate
|
|
|||
 |
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
IUPAC names
Antimony pentachloride
Antimony(V) chloride |
|||
| Other names
Antimonic chloride
Antimony perchloride |
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.729 | ||
| EC Number | 231-601-8 | ||
|
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number | CC5075000 | ||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| Cl5Sb | |||
| Molar mass | 299.01 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | colorless or reddish-yellow (fuming) liquid, oily | ||
| Odor | pungent, offensive | ||
| Density | 2.336 g/cm3 (20 °C) 2.36 g/cm3 (25 °C) |
||
| Melting point | 2.8 °C (37.0 °F; 275.9 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 140 °C (284 °F; 413 K) decomposes from 106 °C 79 °C (174 °F; 352 K) at 22 mmHg 92 °C (198 °F; 365 K) at 30 mmHg |
||
| reacts | |||
| Solubility | soluble in alcohol, HCl, tartaric acid, CHCl3, CS2, CCl4 | ||
| Solubility in selenium(IV) oxychloride | 62.97 g/100 g (25 °C) | ||
| Vapor pressure | 0.16 kPa (25 °C) 4 kPa (40 °C) 7.7 kPa (100 °C) |
||
| -120.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
|
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.59255 | ||
| Viscosity | 2.034 cP (29.4 °C) 1.91 cP (35 °C) |
||
| Structure | |||
| Trigonal bipyramidal | |||
| 0 D | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
| 120.9 J/mol·K (gas) | |||
|
Std molar
entropy (S |
295 J/mol·K | ||
|
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH |
-437.2 kJ/mol | ||
|
Gibbs free energy (ΔfG˚)
|
-345.35 kJ/mol | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS pictograms |
 
|
||
| GHS signal word | Danger | ||
| H314, H411 | |||
| P273, P280, P305+351+338, P310 | |||
| Inhalation hazard | Toxic | ||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| Flash point | 77 °C (171 °F; 350 K) | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
1115 mg/kg, (rat, oral) | ||
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |||
|
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 0.5 mg/m3 (as Sb) | ||
|
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 0.5 mg/m3 (as Sb) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
|
Other anions
|
Antimony pentafluoride | ||
|
Other cations
|
Phosphorus pentachloride | ||
|
Related compounds
|
Antimony trichloride | ||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
Antimony pentachloride is a chemical compound with the formula SbCl5. It is a colourless oil, but typical samples are yellowish due to impurities. Owing to its tendency to hydrolyse to hydrochloric acid, SbCl5 is a highly corrosive substance and carbonizes non-fluorinated plastics.
Antimony pentachloride is prepared by passing chlorine gas into molten antimony trichloride:
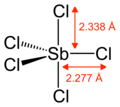
Gaseous SbCl5 has a trigonal prismatic structure.
Antimony pentachloride hydrolyses to give hydrochloric acid and antimony oxychlorides. This reaction is suppressed in the presence of a large excess of chloride, owing to the formation of the hexachloroantimonate complex ion:
The mono- and tetrahydrates are known, SbCl5·H2O SbCl5·4 H2O.
This compound forms adducts with many Lewis bases. It is used as the standard Lewis acid in the Gutmann scale of Lewis basicity.
It is also a strong oxidizing agent.
Antimony pentachloride is used as a polymerization catalyst and for the chlorination of organic compounds.
Antimony pentachloride is a highly corrosive substance that should be stored away from heat and moisture. It is a chlorinating agent and, in the presence of moisture, it releases hydrogen chloride gas. Because of this, it may etch even stainless-steel tools (such as needles), if handled in a moist atmosphere. It should not be handled with non-fluorinated plastics (such as plastic syringes, plastic septa, or needles with plastic fittings), since it melts and carbonizes plastic materials.
Manufacturer and supplier..... Chemical & Metal Industries, Inc. Hudson, CO 80642 (303)-536-9800
...
Wikipedia