Greater snow goose
| Snow goose | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| A. c. caerulescens white morph | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Anseriformes |
| Family: | Anatidae |
| Genus: | Anser |
| Species: | A. caerulescens |
| Binomial name | |
|
Anser caerulescens (Linnaeus, 1758) |
|
| Subspecies | |
 |
|
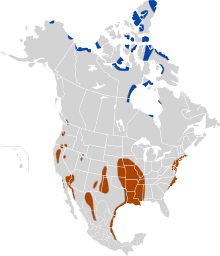
| Snow goose range: Breeding range Wintering range | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
The snow goose (Anser caerulescens), consisting of both a white phase and blue phase (Blue Goose), is a North American species of goose commonly collectively referred to as "light geese". Its name derives from the typically white plumage. Many taxonomic authorities placed this species and the other "white geese" in the Chen genus,. Most authorities now follow the traditional treatment of placing these species in the "gray goose" genus Anser. The scientific name is from the Latin anser, "goose", and caerulescens, "bluish", derived from caeruleus , "dark blue".
This goose breeds north of the timberline in Greenland, Canada, Alaska, and the northeastern tip of Siberia, and spends winters in warm parts of North America from southwestern British Columbia through parts of the United States to Mexico. They fly as far south as Texas and Mexico during winter, and return to nest on the Arctic tundra each spring. It is a rare vagrant to Europe, but a frequent escape from collections and an occasional feral breeder. Snow geese are visitors to the British Isles where they are seen regularly among flocks of barnacle, Brent and Greenland white-fronted geese. There is also a feral population in Scotland from which many vagrant birds in Britain seem to derive.
In Central America, vagrants are frequently encountered during winter.
...
Wikipedia

