Ethylene glycol poisoning
| Ethylene glycol poisoning | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Ethylene glycol toxicity |
 |
|
| Ethylene glycol | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | emergency medicine |
| ICD-10 | T51.8 |
| eMedicine | emerg/177 |
Ethylene glycol poisoning is poisoning caused by drinking ethylene glycol. Early symptoms include intoxication, vomiting and abdominal pain. Later symptoms may include a decreased level of consciousness, headache, and seizures. Long term outcomes may include kidney failure and brain damage. Toxicity and death may occur even after drinking a small amount.
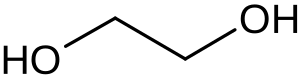
Ethylene glycol is a colorless, odorless, sweet liquid, commonly found in antifreeze. It may be drunk accidentally or purposefully in an attempt to cause death. When broken down by the body it results in glycolic acid and oxalic acid which cause most of the toxicity. The diagnosis may be suspected when calcium oxalate crystals are seen in the urine or when acidosis or an increased osmol gap is present in the blood. Diagnosis may be confirmed by measuring ethylene glycol levels in the blood; however, many hospitals do not have the ability to perform this test.
Early treatment increases the chance of a good outcome. Treatment consists of stabilizing the person, followed by the use of an antidote. The preferred antidote is fomepizole with ethanol used if this is not available. Hemodialysis may also be used in those where there is organ damage or a high degree of acidosis. Other treatments may include sodium bicarbonate, thiamine, and magnesium.
...
Wikipedia
