EPSP synthase
| EPSP Synthase (3-phosphoshikimate 1-carboxyvinyltransferase) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
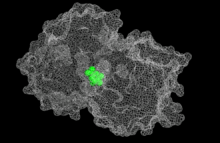
EPSP synthase liganded with shikimate.
|
|||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 2.5.1.19 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 9068-73-9 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / EGO | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Search | |
|---|---|
| PMC | articles |
| PubMed | articles |
| NCBI | proteins |
| EPSP synthase (3-phosphoshikimate 1-carboxyvinyltransferase) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
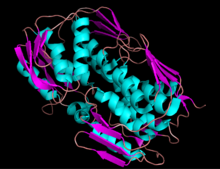
Ribbon diagram of EPSP synthase
|
|||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | EPSP_synthase | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00275 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR001986 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00097 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1eps | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 1eps | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Available protein structures: | |
|---|---|
| Pfam | structures |
| PDB | RCSB PDB; PDBe; PDBj |
| PDBsum | structure summary |
5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate (EPSP) synthase is an enzyme produced by plants and microorganisms. It catalyzes the chemical reaction:
Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) and 3-phospho-shikimate, whereas its two products are phosphate and 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate.
It is the biological target of the herbicide glyphosate, and a glyphosate-resistant version of this gene has been used in genetically modified crops.
The enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, to be specific those transferring aryl or alkyl groups other than methyl groups. The systematic name of this enzyme class is phosphoenolpyruvate:3-phosphoshikimate 5-O-(1-carboxyvinyl)-transferase. Other names in common use include:
EPSP synthase is a monomeric enzyme with a molecular mass of about 46,000. It is composed of two domains, which are joined by protein strands. This strand acts as a hinge, and can bring the two protein domains closer together. When a substrate binds to the enzyme, ligand bonding causes the two parts of the enzyme to clamp down around the substrate in the active site.
EPSP synthase has been divided into two groups according to glyphosate sensitivity. Class I enzyme, contained in plants and in some bacteria, is inhibited at low micromolar glyphosate concentrations, whereas class II enzyme, found in other bacteria, is resistant to inhibition by glyphosate.
EPSP synthase participates in the biosynthesis of the aromatic amino acids phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan via the shikimate pathway in bacteria, fungi, and plants. EPSP synthase is produced only by plants and micro-organisms; the gene coding for it is not in the mammalian genome.Gut flora of some animals contain EPSPS.
...
Wikipedia
