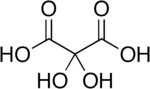
Dihydroxymalonic acid
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
2,2-Dihydroxypropanedioic acid
|
|
| Other names
Dihydroxypropanedioic acid
Mesoxalic acid monohydrate Oxomalonic acid monohydrate Ketomalonic acid monohydrate |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.372 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C3H4O6 | |
| Molar mass | 136.06 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 119 to 120 °C (246 to 248 °F; 392 to 393 K) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Dihydroxymalonic acid is an organic compound with formula C3H4O6 or HO-(C=O)-C(OH)2-(C=O)-OH, found in some plants such as alfalfa and in beet molasses.
The compound may also be called dihydroxymesoxalic acid, dihydroxypropanedioic acid. It can be viewed as a hydrate derivative of mesoxalic acid, and indeed it is often called mesoxalic acid monohydrate and other silmilar names. This compound is unusual in containing stable geminal hydroxy groups.
Dihydroxymalonic acid is a water-soluble white solid. It crystallizes in deliquescent prisms that melt between 113 °C and 121 °C without loss of water. It has been used in medical research as a hypoglycemic agent and was patented in the United States in 1997 as a fast-acting antidote to cyanide poisoning.
Dihydroxymalonic acid can be obtained synthetically by hydrolysis of alloxan with baryta water, by warming caffuric acid with lead acetate solution, by electrolysis of tartaric acid in alkaline solution, or from glycerin diacetate and concentrated nitric acid in the cold. The product can be obtained also by oxidation of tartronic acid or glycerol.
Like typical hydrated ketonic acids, it is reduced in aqueous solution by sodium amalgam to tartronic acid, and also combines with phenylhydrazine and hydroxylamine. It reduces ammoniacal silver solutions. When heated with urea to 100 °C, it forms allantoin. By continued boiling of its aqueous solution it is decomposed into carbon dioxide and glyoxylic acid.
...
Wikipedia
