Diethylzinc
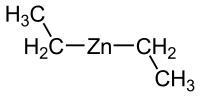 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
diethylzinc
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
557-20-0 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:51496 |
| ChemSpider |
10413128 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.330 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| (C2H5)2Zn | |
| Molar mass | 123.50 g/mol |
| Density | 1.205 g/mL |
| Melting point | −28 °C (−18 °F; 245 K) |
| Boiling point | 117 °C (243 °F; 390 K) |
| Reacts violently | |
| Hazards | |
|
EU classification (DSD)
|
|
| NFPA 704 | |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Diethylzinc (C2H5)2Zn, or DEZ, is a highly pyrophoric organozinc compound consisting of a zinc center bound to two ethyl groups. This colourless liquid is an important reagent in organic chemistry and available commercially as a solution in hexanes, heptane, or toluene.
Edward Frankland first reported the compound in 1848 from zinc and ethyl iodide, the first organozinc compound discovered. He improved the synthesis by using diethyl mercury as starting material The contemporary synthesis consists of the reaction of a 1:1 mixture of ethyl iodide and ethyl bromide with a zinc-copper couple, a source of reactive zinc.
The compound crystallizes in a tetragonal body-centered unit cell of space group symmetry I41md. In the solid-state diethylzinc shows nearly linear Zn centres. The Zn-C bonds measure 194.8(5) pm, while the C-Zn-C angle is slightly bent with 176.2(4)°. The structure of the gas-phase shows a very similar Zn-C distance (195.0(2) pm).
Despite its highly pyrophoric nature, diethylzinc is an important chemical reagent. It is used in organic synthesis as a source of the ethyl carbanion in addition reactions to carbonyl groups. For example, the asymmetric addition of an ethyl group to benzaldehyde and imines. Additionally, it is commonly used in combination with diiodomethane as a Simmons-Smith reagent to convert alkenes into cyclopropyl groups. It is less nucleophilic than related alkyllithium and Grignard reagents, so it may be used when a "softer" nucleophile is needed. It is also used extensively in materials science chemistry as a zinc source in the synthesis of nanoparticles. Particularly in the formation of the zinc sulfide shell for core/shell-type quantum dots. While in polymer chemistry, it can be used as part of the catalyst for a chain shuttling polymerization reaction, whereby it participates in living polymerization.
...
Wikipedia

