Cutch State
| Cutch State | ||||||||||||
| કચ્છ રિયાસત | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
|
Cutch State, 1878
|
||||||||||||
| Capital | Lakhiarviro (1147―1548) Bhuj (1549―1948) |
|||||||||||
| Government | Not specified | |||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||
| • | Established | 1147 | ||||||||||
| • | came under Cutch Agency of Company | 1819 | ||||||||||
| • | merged into India as Kutch State | 1948 | ||||||||||
| Area | ||||||||||||
| • | 1901 | 45,630 km² (17,618 sq mi) | ||||||||||
| Population | ||||||||||||
| • | 1901 est. | 488,022 | ||||||||||
| Density | 10.7 /km² (27.7 /sq mi) | |||||||||||
| Currency | Kutch kori | |||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Today part of | Kutch district of Gujarat, India | |||||||||||
| Warning: Value not specified for "" | ||||||||||||
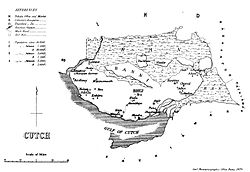
Cutch, also spelled Kutch or Kachchh, was a relatively large Indian princely state during the British Raj. Its territories covered the present day Kutch region of Gujarat north of the Gulf of Kutch. Bordered by Sindh in the north, Cutch State was one of the few princely states with a coastline.
The state had an area of 17,616 square miles (45,630 km2) and a population estimated at 488,022 in 1901. During the British Raj, the state was part of the Cutch Agency and later the Western India States Agency within the Bombay Presidency. The rulers maintained an army of 354 cavalry, 1,412 infantry and 164 guns.
Cutch's flag was a red rectangular with images of a white elephant and Bhujia Fort in the centre and the word BHOOJ inscribed above the fort in white. The motto: Courage and Confidence was written below in a white ribbon.
A predecessor state known as the Kingdom of Kutch was founded around 1147 by Lakho Jadani of the Samma tribe who had arrived from Sindh. He was adopted by Jam Jada and hence known as Lakho Jadani. He ruled Eastern Cutch from 1147−1175 from a new capital, which he named Lakhiarviro (near present-day Nakhatrana) after his twin brother Lakhiar. Prior to this time, Eastern Cutch was ruled by the Chawda dynasty, whose last noted ruler was Vagham Chawda, who was killed in the 13th century by his nephews Mod and Manai of the Jadeja clan. At the same time, Central and Western Kutch were under the control of different tribes such as the Kathi, Chaulukya and Waghela. After the death of Raydhan Ratto in 1215 his territories were divided between his four sons. Othaji, Dedaji, Hothiji and Gajanji and they were given the Kutch territories of Lakhirviro, Kanthkot, Gajod and Bara respectively.
...
Wikipedia