Chhuikhadan State
| Chhuikhadan State छुईखदान रियासत |
|||||
| Princely State of British India | |||||
|
|||||
|
Flag |
|||||
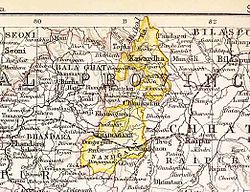
| Chhuikhadan State in the Imperial Gazetteer of India | |||||
| History | |||||
| • | Established | 1750 | |||
| • | Accession to the Indian Union | 1948 | |||
| Area | |||||
| • | 1901 | 396 km2(153 sq mi) | |||
| Population | |||||
| • | 1901 | 26,368 | |||
| Density | 66.6 /km2 (172.5 /sq mi) | ||||
| Today part of | Rajnandgaon district, Chhattisgarh | ||||
Flag
Chhuikhadan (also known as Kondka) was a small princely state of British India, which later formed part of Chhattisgarh States Agency. The state flag was a purple triangle.
The state consisted of an area of 320 square miles, of which 27,907 acres were cultivated, and 48,538 acres cultivable. There were 120 villages in 1870 and the population was 13,281. In 1941 the state had a population of 32,731 people. The capital of the State was Chhuikhadan
The chief was a Kunwar and belonged to a Bairagi dynasty known as Mahants. The chiefs of Chhuikhadan were originally under the Bhonsles of Nagpur, the first Chief being Mahant Rup Das in 1750. However, after defeat of Marathas, they were recognized by British as feudatory chiefs in 1865 conferring the title and sanad to Mahant Laxman Das. Mahant Ritu Purna Kishor Das, the last ruling Chief of Chhuikhadan signed the accession of the State to the Union of India on 1 February 1948.
Coordinates: 21°32′N 80°59′E / 21.53°N 80.98°E
...
Wikipedia