Cellulitis
| Cellulitis | |
|---|---|
 |
|
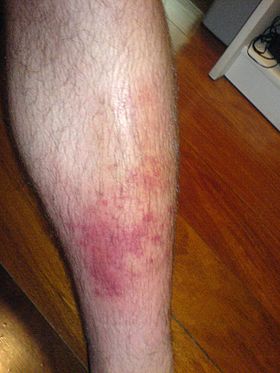
| Skin cellulitis | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
| Symptoms | redness, heat, pain |
| Duration | 7-10 days |
| Causes | bacteria |
| Risk factors | weak immune system, diabetes, poor circulation |
| Differential diagnosis | deep vein thrombosis, stasis dermatitis, Lyme disease |
| Medication | antibiotics |
| Frequency | 37 million per year (global) |
| Deaths | 30,000 per year (global) |
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
Cellulitis is a bacterial infection involving the inner layers of the skin. It specifically affects the dermis and subcutaneous fat. Signs and symptoms include an area of redness which increases in size over a few days. The borders of the area of redness are generally not sharp and the skin may be swollen. While the redness often turns white when pressure is applied, this is not always the case. The area of infection is usually painful.Lymphatic vessels may occasionally be involved, and the person may have a fever and feel tired.
The legs and face are the most common sites involved, though cellulitis can occur on any part of the body. The leg is typically affected following a break in the skin. Other risk factors include obesity, leg swelling, and old age. For facial infections, a break in the skin beforehand is not usually the case. The bacteria most commonly involved are and Staphylococcus aureus.
In contrast to cellulitis, erysipelas is a bacterial infection involving the more superficial layers of the skin, present with an area of redness with well-defined edges, and more often is associated with a fever. Diagnosis is usually based on the presenting signs and symptoms, while cell culture is rarely possible. Before making a diagnosis, more serious infections such as an underlying bone infection or necrotizing fasciitis should be ruled out.
Treatment with antibiotics taken by mouth, such as cephalexin, amoxicillin, or cloxacillin, is often used. In those who are seriously allergic to penicillin, erythromycin or clindamycin may be used. When methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) is a concern, doxycycline or trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole may, in addition, be recommended. Concern is related to the presence of pus or previous MRSA infections. Elevating the infected area may be useful, as may pain killers.
...
Wikipedia
