Casava
| Cassava | |
|---|---|
 |
|
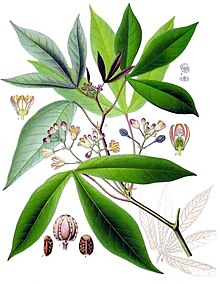
| Leaves of the cassava plant | |
 |
|
| A manioc tuber | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (unranked): | Angiosperms |
| (unranked): | Eudicots |
| (unranked): | Rosids |
| Order: | Malpighiales |
| Family: | Euphorbiaceae |
| Subfamily: | Crotonoideae |
| Tribe: | Manihoteae |
| Genus: | Manihot |
| Species: | M. esculenta |
| Binomial name | |
|
Manihot esculenta Crantz |
|
| Synonyms | |
|
|
| Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) | |
|---|---|
| Energy | 160 kcal (670 kJ) |
|
38.1 g
|
|
| Sugars | 1.7 g |
| Dietary fiber | 1.8 g |
|
0.3 g
|
|
|
1.4 g
|
|
| Vitamins | |
| Thiamine (B1) |
(8%)
0.087 mg |
| Riboflavin (B2) |
(4%)
0.048 mg |
| Niacin (B3) |
(6%)
0.854 mg |
| Vitamin B6 |
(7%)
0.088 mg |
| Folate (B9) |
(7%)
27 μg |
| Vitamin C |
(25%)
20.6 mg |
| Minerals | |
| Calcium |
(2%)
16 mg |
| Iron |
(2%)
0.27 mg |
| Magnesium |
(6%)
21 mg |
| Phosphorus |
(4%)
27 mg |
| Potassium |
(6%)
271 mg |
| Sodium |
(1%)
14 mg |
| Zinc |
(4%)
0.34 mg |
| Other constituents | |
| Water | 60 g |
|
|
|
|
|
| Percentages are roughly approximated using US recommendations for adults. | |
Manihot esculenta (commonly called cassava (/kəˈsɑːvə/),yuca, manioc, "mandioca" and Brazilian arrowroot) is a woody shrub native to South America of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae. It is extensively cultivated as an annual crop in tropical and subtropical regions for its edible starchy tuberous root, a major source of carbohydrates. Though it is often called yuca in Spanish and in the United States, it differs from the yucca, an unrelated fruit-bearing shrub in the family Asparagaceae. Cassava, when dried to a powdery (or pearly) extract, is called tapioca; its fermented, flaky version is named garri.
Cassava is the third-largest source of food carbohydrates in the tropics, after rice and maize. Cassava is a major staple food in the developing world, providing a basic diet for over half a billion people. It is one of the most drought-tolerant crops, capable of growing on marginal soils. Nigeria is the world's largest producer of cassava, while Thailand is the largest exporter of dried cassava.
Cassava is classified as either sweet or bitter. Like other roots and tubers, both bitter and sweet varieties of cassava contain antinutritional factors and toxins, with the bitter varieties containing much larger amounts. It must be properly prepared before consumption, as improper preparation of cassava can leave enough residual cyanide to cause acute cyanide intoxication,goiters, and even ataxia, partial paralysis, or death. The more toxic varieties of cassava are a fall-back resource (a "food security crop") in times of famine or food insecurity in some places. Farmers often prefer the bitter varieties because they deter pests, animals, and thieves.
...
Wikipedia
