Camphoraceous
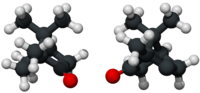
 (R)- (left) and (S)-camphor
|
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
1,7,7-Trimethylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-one
|
|
|
Systematic IUPAC name
1,7,7-Trimethylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-one
|
|
| Other names
2-Bornanone; Bornan-2-one; 2-Camphanone; Formosa
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
|
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| 3DMet | B04729 |
| 1907611 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.860 |
| EC Number | 200-945-0 |
| 83275 | |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Camphor |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number | EX1225000 |
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2717 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C10H16O | |
| Molar mass | 152.24 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White, translucent crystals |
| Odor | fragrant and penetrating |
| Density | 0.992 g cm−3 |
| Melting point | 175 to 177 °C (347 to 351 °F; 448 to 450 K) |
| Boiling point | 209 °C (408 °F; 482 K) |
| 1.2 g dm−3 | |
| Solubility in acetone | ~2500 g dm−3 |
| Solubility in acetic acid | ~2000 g dm−3 |
| Solubility in diethyl ether | ~2000 g dm−3 |
| Solubility in chloroform | ~1000 g dm−3 |
| Solubility in ethanol | ~1000 g dm−3 |
| log P | 2.089 |
| Vapor pressure | 4 mmHg (at 70 °C) |
|
Chiral rotation ([α]D)
|
+44.1° |
| -103·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Pharmacology | |
| C01EB02 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
|
EU classification (DSD)
|
|
| R-phrases | R11 R22 R36/37/38 |
| S-phrases | S16 S26 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | 54 °C (129 °F; 327 K) |
| 466 °C (871 °F; 739 K) | |
| Explosive limits | 0.6%-3.5% |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
1310 mg/kg (oral, mouse) |
|
LDLo (lowest published)
|
800 mg/kg (dog, oral) 2000 mg/kg (rabbit, oral) |
|
LCLo (lowest published)
|
400 mg/m3 (mouse, 3 hr) |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
|
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 2 mg/m3 |
|
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 2 mg/m3 |
|
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
200 mg/m3 |
| Related compounds | |
|
Related Ketones
|
Fenchone, Thujone |
|
Related compounds
|
Camphene, Pinene, Borneol, Isoborneol, Camphorsulfonic acid |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Camphor (/ˈkæmfər/) is a waxy, flammable, white or transparent solid with a strong aroma. It is a terpenoid with the chemical formula C10H16O. It is found in the wood of the camphor laurel (Cinnamomum camphora), a large evergreen tree found in Asia (particularly in Sumatra, Indonesia and Borneo) and also of the unrelated kapur tree, a tall timber tree from the same region. It also occurs in some other related trees in the laurel family, notably Ocotea usambarensis. The oil in rosemary leaves (Rosmarinus officinalis), in the mint family, contains 10 to 20% camphor, while camphorweed (Heterotheca) only contains some 5%. Camphor can also be synthetically produced from oil of turpentine. It is used for its scent, as an ingredient in cooking (mainly in India), as an embalming fluid, for medicinal purposes, and in religious ceremonies. A major source of camphor in Asia is camphor basil (the parent of African blue basil).
...
Wikipedia

