Cacao plantation
| Theobroma cacao | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Cacao fruits on the tree | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (unranked): | Angiosperms |
| (unranked): | Eudicots |
| (unranked): | Rosids |
| Order: | Malvales |
| Family: | Malvaceae |
| Genus: | Theobroma |
| Species: | T. cacao |
| Binomial name | |
|
Theobroma cacao L. |
|
| Synonyms | |
|
|
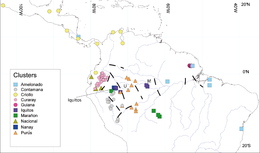
Map showing genetic clusters of Theobroma cacao
|
|
| NCBI genome ID | 572 |
|---|---|
| Ploidy | diploid |
| Genome size | 345.99 Mb |
| Number of chromosomes | 10 pairs |
| Year of completion | 2010 |
Theobroma cacao is the taxonomic classification for the plant also called the cacao tree and the cocoa tree, which is a small (4–8 m (13–26 ft) tall) evergreen tree in the family Malvaceae, native to the deep tropical regions of Central and South America. Its seeds, cocoa beans, are used to make cocoa mass, cocoa powder, confectionery, ganache and chocolate.
Leaves are alternate, entire, unlobed, 10–40 cm (3.9–15.7 in) long and 5–20 cm (2.0–7.9 in) broad.
The flowers are produced in clusters directly on the trunk and older branches; this is known as cauliflory. The flowers are small, 1–2 cm (0.39–0.79 in) diameter, with pink calyx. The floral formula is ✶ K5 C5 A(5°+5²) G(5). While many of the world's flowers are pollinated by bees (Hymenoptera) or butterflies/moths (Lepidoptera), cacao flowers are pollinated by tiny flies, Forcipomyia midges in the subfamily Forcipomyiinae. Having the natural pollinator Forcipomyia midges for Theobroma cacao was shown to have more fruit production than using artificial pollinators. The fruit, called a cacao pod, is ovoid, 15–30 cm (5.9–11.8 in) long and 8–10 cm (3.1–3.9 in) wide, ripening yellow to orange, and weighs about 500 g (1.1 lb) when ripe. The pod contains 20 to 60 seeds, usually called "beans", embedded in a white pulp. The seeds are the main ingredient of chocolate, while the pulp is used in some countries to prepare refreshing juice, smoothies, jelly, and nata. The fermented pulp, until recently discarded in Ecuador, the Dominican Republic, and Peru, is now being distilled there into a popular alcoholic beverage sold in the United States. Each seed contains a significant amount of fat (40–50%) as cocoa butter. Their most noted active constituent is theobromine, a compound similar to caffeine.
...
Wikipedia
