Bradykinin
 |
|
 |
|
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
|
58-82-2 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:3165 |
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL406291 |
| ChemSpider |
388341 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.362 |
| 649 | |
| MeSH | Bradykinin |
| PubChem | 439201 |
| UNII |
S8TIM42R2W |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C50H73N15O11 | |
| Molar mass | 1,060.23 g·mol−1 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
| kininogen 1 | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | KNG1 |
| Alt. symbols | KNG, BDK |
| Entrez | 3827 |
| HUGO | 6383 |
| OMIM | 612358 |
| RefSeq | NM_001102416 |
| UniProt | P01042 |
| Other data | |
| Locus | Chr. 3 q21-qter |
| Bradykinin | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Bradykinin | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF06753 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR009608 | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Available protein structures: | |
|---|---|
| Pfam | structures |
| PDB | RCSB PDB; PDBe; PDBj |
| PDBsum | structure summary |
Bradykinin is an inflammatory mediator. It is a peptide that causes blood vessels to dilate (enlarge), and therefore causes blood pressure to fall. A class of drugs called ACE inhibitors, which are used to lower blood pressure, increase bradykinin (by inhibiting its degradation) further lowering blood pressure. Bradykinin dilates blood vessels via the release of prostacyclin, nitric oxide, and Endothelium-Derived Hyperpolarizing Factor.
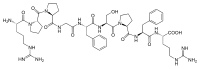
Bradykinin is a physiologically and pharmacologically active peptide of the kinin group of proteins, consisting of nine amino acids.
Bradykinin is a 9-amino acid peptide chain. The amino acid sequence of bradykinin is: Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser-Pro-Phe-Arg (RPPGFSPFR). Its empirical formula is therefore C50H73N15O11.
The kinin-kallikrein system makes bradykinin by proteolytic cleavage of its kininogen precursor, high-molecular-weight kininogen (HMWK or HK), by the enzyme kallikrein. Moreover, there is compelling evidence that plasmin, a fibrinolytic enzyme, is able to generate bradykinin after HMWK cleavage.
...
Wikipedia
