Baghelkhand Agency
| Bagelkhand Agency | |||||
| Agency of British India | |||||
|
|||||
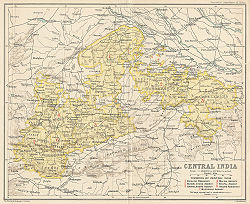
| Map of the Central India Agency with the Bagelkhand Agency at the eastern end | |||||
| History | |||||
| • | Established | 1871 | |||
| • | Disestablished | 1933 | |||
| Area | |||||
| • | 1901 | 37,100 km2(14,324 sq mi) | |||
| Population | |||||
| • | 1901 | 1,555,024 | |||
| Density | 41.9 /km2 (108.6 /sq mi) | ||||
The Bagelkhand Agency was a British political unit which managed the relations of the British with a number of autonomous princely states existing outside British India, namely Rewa and eleven minor states, of which the more important were Maihar, Nagod —with its capital at Uuchahara— and Sohawal. The less important states included Jaso State, Kothi, Baraundha, also known as Patharkachhar, as well as the Kalinjar Chaubes —consisting of the princely estates of Paldeo, Kamta-Rajaula, Taraon, Pahra and Bhaisaunda.
The Agency was established in March 1871 and was named after the Bagelkhand region. From 1871 to 1933 the Agency was under the political supervision of the Governor-General of India's Agent for Central India, and under the direct supervision of a political Agent who was also the appointed Resident to Rewa State, residing ordinarily at Satna or Rewa.
The total area was 14,323 square miles (37,100 km2), and the population in 1901 was 1,555,024, a decrease of 11% over the previous census ten years before, largely due to the results of famine. The rainfall was very deficient in 1895-1897, causing a famine in 1897; and in 1899-1900 there was another drought in some states. In 1931, the eleven smaller states were transferred to the Bundelkhand Agency, and in 1933 the agency was dissolved, when Rewa State joined the Indore Residency.
...
Wikipedia