Australian green tree frog
| Litoria caerulea | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Amphibia |
| Order: | Anura |
| Family: | Hylidae |
| Subfamily: | Pelodryadinae |
| Genus: | Litoria |
| Species: | L. caerulea |
| Binomial name | |
|
Litoria caerulea (White, 1790) |
|
 |
|
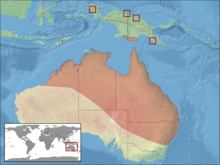
| Distribution | |
| Synonyms | |
|
List
|
|
The Australian green tree frog, simply green tree frog in Australia, White's tree frog, or dumpy tree frog (Litoria caerulea) is a species of tree frog native to Australia and New Guinea, with introduced populations in the United States and New Zealand, though the latter is believed to have died out. The species belongs to the genus Litoria. It is morphologically similar to some other members of the genus, particularly the magnificent tree frog (L. splendida) and the white-lipped tree frog (L. infrafrenata).
Larger than most Australian frogs, the Australian green tree frog reaches 10 cm (4 in) or more in length. Its average lifespan in captivity, about 16 years, is long compared with most frogs. Docile and well suited to living near human dwellings, Australian green tree frogs are often found on window sills or inside houses, eating insects drawn by the light. The green tree frog screams when it is in danger to scare off its foe, and squeaks when it is touched.
Due to its appearance and behavioral traits, the green tree frog is a popular exotic pet throughout the world. The skin secretions of the frog have antibacterial and antiviral properties that may prove useful in pharmaceutical preparations and which have rendered it relatively immune to the population declines being experienced by many species of amphibian. It is a common species and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed its conservation status as being "least concern".
The Australian green tree frog is a member of the New World tree frog family Hylidae and is placed in the subfamily "Pelodryadinae" which is endemic to Australia and New Guinea and includes about 160 species in the genera Cyclorana, Litoria and Nyctimystes. Frogs in the genus Litoria are distinguishable from other tree frogs by the presence of horizontal irises and the lack of pigmentation on the eyelids. The common name of the species, "White's tree frog", is in honor of John White's first description in 1790. The green tree frog was the first Australian frog to be scientifically described; the original specimen found its way into the collection of Sir Joseph Banks, but was destroyed when the Hunterian Museum at the Royal College of Surgeons in London was bombed in World War II.
...
Wikipedia

