Atp synthesis
| ATP Synthase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
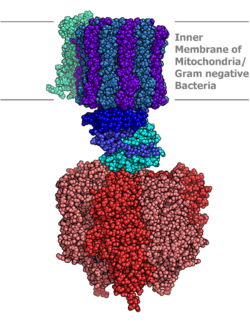
Molecular model of ATP synthase determined by X-ray crystallography
|
|||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 3.6.3.14 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 9000-83-3 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / EGO | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Search | |
|---|---|
| PMC | articles |
| PubMed | articles |
| NCBI | proteins |
ATP synthase is an enzyme that creates the energy storage molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is the most commonly used "energy currency" of cells for most organisms. It is formed from adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate (Pi). The overall reaction catalyzed by ATP synthase is:
The formation of ATP from ADP and Pi is energetically unfavorable and would normally proceed in the reverse direction. In order to drive this reaction forward, ATPase couples ATP synthesis during cellular respiration to an electrochemical gradient created by the difference in proton (H+) concentration across the membrane in eukaryotes or the plasma membrane in bacteria. During photosynthesis in plants, ATP is synthesized by ATPase using a proton gradient created in the thylakoid lumen through the thylakoid membrane and into the chloroplast stroma.
ATP synthase consists of two main subunits, FO and F1, which has a rotational motor mechanism allowing for ATP production.
The F1 fraction derives its name from the term "Fraction 1" and FO (written as a subscript letter "o", not "zero") derives its name from being the binding fraction for oligomycin, a type of naturally-derived antibiotic that is able to inhibit the FO unit of ATP synthase. These functional regions consist of different protein subunits — refer to tables.
Located within the thylakoid membrane and the , ATP synthase consists of two regions FO and F1. FO causes rotation of F1 and is made of c-ring and subunits a, b, d, F6. F1 is made of subunits. F1 has a water soluble par that can hydrolyze ATP. FO on the other hand has mainly hydrophobic regions. FO F1 creates a pathway for protons movement across the membrane.
...
Wikipedia

