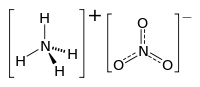
Ammonia nitrate
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Ammonium nitrate
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.026.680 |
| RTECS number | BR9050000 |
| UNII | |
| UN number |
0222 – with > 0.2% combustible substances 1942 – with <= 0.2% combustible substances 2067 – fertilizers 2426 – liquid |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| NH4NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 80.043 g/mol |
| Appearance | white/grey solid |
| Density | 1.725 g/cm3 (20 °C) |
| Melting point | 169.6 °C (337.3 °F; 442.8 K) |
| Boiling point | approx. 210 °C; decomposes |
| 118 g/100 ml (0 °C) 150 g/100 ml (20 °C) 297 g/100 ml (40 °C) 410 g/100 ml (60 °C) 576 g/100 ml (80 °C) 1024 g/100 ml (100 °C) |
|
| -33.6·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Structure | |
| trigonal | |
| Explosive data | |
| Shock sensitivity | very low |
| Friction sensitivity | very low |
| Detonation velocity | 5270 m/s |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Explosive |
| Safety data sheet | ICSC 0216 |
|
EU classification (DSD) (outdated)
|
|
| NFPA 704 | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
2085–5300 mg/kg (oral in rats, mice) |
| Related compounds | |
|
Other anions
|
Ammonium nitrite |
|
Other cations
|
Sodium nitrate Potassium nitrate Hydroxylammonium nitrate |
|
Related compounds
|
Ammonium perchlorate |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Ammonium nitrate is a chemical compound, the nitrate salt of the ammonium cation. It has the chemical formula NH4NO3, simplified to N2H4O3. It is a white crystal solid and is highly soluble in water. It is predominantly used in agriculture as a high-nitrogen fertilizer. Its other major use is as a component of explosive mixtures used in mining, quarrying, and civil construction. It is the major constituent of ANFO, a popular industrial explosive which accounts for 80% of explosives used in North America; similar formulations have been used in improvised explosive devices. Many countries are phasing out its use in consumer applications due to concerns over its potential for misuse.
Ammonium nitrate is found as a natural mineral (ammonia nitre—the ammonium analogue of saltpetre and other nitre minerals such as sodium nitrate) in the driest regions of the Atacama Desert in Chile, often as a crust on the ground and/or in conjunction with other nitrate, chlorate, iodate, and halide minerals. Ammonium nitrate was mined there in the past, but virtually 100% of the chemical now used is synthetic.
The industrial production of ammonium nitrate entails the acid-base reaction of ammonia with nitric acid:
Ammonia is used in its anhydrous form (i.e., gas form) and the nitric acid is concentrated. This reaction is violent owing to its highly exothermic nature. After the solution is formed, typically at about 83% concentration, the excess water is evaporated to an ammonium nitrate (AN) content of 95% to 99.9% concentration (AN melt), depending on grade. The AN melt is then made into "prills" or small beads in a spray tower, or into granules by spraying and tumbling in a rotating drum. The prills or granules may be further dried, cooled, and then coated to prevent caking. These prills or granules are the typical AN products in commerce.
...
Wikipedia

