Amelogenesis imperfecta
| Amelogenesis imperfecta | |
|---|---|
 |
|
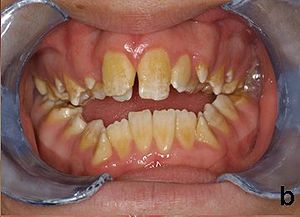
| Amelogenesis imperfecta, hypoplastic type. Note the association of pitted enamel and open bite. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| ICD-10 | K00.5 |
| ICD-9-CM | 520.5 |
| DiseasesDB | 31408 |
| MedlinePlus | 001578 |
Amelogenesis imperfecta (AI) presents with a rare abnormal formation of the enamel or external layer of the crown of teeth. Enamel is composed mostly of mineral, that is formed and regulated by the proteins in it. Amelogenesis imperfecta is due to the malfunction of the proteins in the enamel: ameloblastin, enamelin, tuftelin and amelogenin.
People afflicted with amelogenesis imperfecta have teeth with abnormal color: yellow, brown or grey; this disorder can afflict any number of teeth of both dentitions. The teeth have a higher risk for dental cavities and are hypersensitive to temperature changes as well as rapid attrition, excessive calculus deposition, and gingival hyperplasia.
Mutations in the AMELX,ENAM,MMP20,KLK-4,FAM83H,WDR72,C4orf26,SLC24A4 LAMB3 and ITGB6 genes have been found to cause amelogenesis imperfecta (non-syndromic form). AMELX and ENAM encode extracellular matrix proteins of the developing tooth enamel and KLK-4 and MMP20 encode proteases that help degrade organic matter from the enamel matrix during the maturation stage of amelogenesis. SLC24A4 encodes a calcium transporter that mediates calcium transport to developing enamel during tooth development. Less is known about the function of other genes implicated in amelogenesis imperfecta.
Researchers expect that mutations in further genes are likely to be identified as causes of amelogenesis imperfecta.Types include:
...
Wikipedia
