Agomelatine
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Melitor, Thymanax, Valdoxan |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| ATC code | N06AX22 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 1% |
| Protein binding | 95% |
| Metabolism | hepatic (90% CYP1A2 and 10% CYP2C9) |
| Biological half-life | 1-2 hours |
| Excretion | Renal (80%, mostly as metabolites) |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number |
138112-76-2 |
| PubChem (CID) | 82148 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 198 |
| DrugBank |
DB06594 |
| ChemSpider |
74141 |
| UNII |
137R1N49AD |
| KEGG |
D02578 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL10878 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.157.896 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
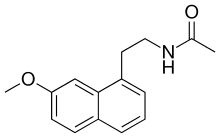
| Formula | C15H17NO2 |
| Molar mass | 243.301 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Agomelatine (BAN, rINN; trade names Valdoxan, Melitor, Thymanax) is a melatonergic antidepressant developed by the pharmaceutical company Servier. It is marketed for the treatment of major depressive disorder, primarily for its relatively favorable side effect profile: it avoids the weight gain, sexual dysfunction, and severe withdrawal associated with the most commonly used classes of antidepressants (SSRIs, SNRIs, tricyclics), while providing similar therapeutic benefit.
Due to its distinctive mechanism of action, agomelatine is also studied for its effects on sleep regulation. Studies report various improvements in general quality of sleep metrics, as well as specific therapeutic benefits in circadian rhythm disorders.
Agomelatine was discovered and developed by the European pharmaceutical company Servier Laboratories Ltd. Servier continued to develop the drug and conduct phase III trials in the European Union.
In March 2005, Servier submitted agomelatine to the European Medicines Agency (EMA) under the trade names Valdoxan and Thymanax. On 27 July 2006, the Committee for Medical Products for Human Use (CHMP) of the EMA recommended a refusal of the marketing authorisation. The major concern was that efficacy had not been sufficiently shown, while there were no special concerns about side effects. In September 2007, Servier submitted a new marketing application to the EMA.
...
Wikipedia
