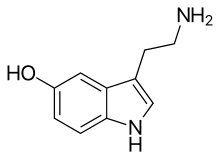
5-hydroxytryptamine
 |
|
| IUPAC name | 3-(2-Aminoethyl)-1H-indol-5-ol |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 5-Hydroxytryptamine, Enteramine; Thrombocytin, 3-(β-Aminoethyl)-5-hydroxyindole, Thrombotonin |
| Abbreviation | 5-HT |
| Sources | raphe nuclei, enterochromaffin cells |
| Targets | system-wide |
| Receptors | 5-HT1, 5-HT2, 5-HT3, 5-HT4, 5-HT5, 5-HT6, 5-HT7 |
| Agonists | SSRIs, MAOIs (indirectly) |
| Precursor | 5-HTP |
| Synthesizing enzyme | Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase |
| Metabolizing enzyme | MAO |
| Database links | |
| CAS Number |
50-67-9 |
| PubChem | CID: 5202 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 5 |
| ChemSpider |
5013 |
| KEGG |
C00780 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC names
5-Hydroxytryptamine or
3-(2-Aminoethyl)indol-5-ol |
|
| Other names
5-Hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT, Enteramine; Thrombocytin, 3-(β-Aminoethyl)-5-hydroxyindole, Thrombotonin
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.054 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Serotonin |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C10H12N2O | |
| Molar mass | 176.215 g/mol |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Melting point | 167.7 °C (333.9 °F; 440.8 K) 121–122 °C (ligroin) |
| Boiling point | 416 ± 30 °C (at 760 Torr) |
| slightly soluble | |
| Acidity (pKa) | 10.16 in water at 23.5 °C |
| 2.98 D | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
750 mg/kg (subcutaneous, rat), 4500 mg/kg (intraperitoneal, rat), 60 mg/kg (oral, rat) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Serotonin (/ˌsɛrəˈtoʊnᵻn, ˌsɪərə-/) or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Biochemically derived from tryptophan, serotonin is primarily found in the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract), blood platelets, and the central nervous system (CNS) of animals, including humans. It is popularly thought to be a contributor to feelings of well-being and happiness.
Approximately 90% of the human body's total serotonin is located in the enterochromaffin cells in the GI tract, where it is used to regulate intestinal movements. The serotonin is secreted luminally and basolaterally which leads to increased serotonin uptake by circulating platelets and activation after stimulation, which gives increased stimulation of myenteric neurons and gastrointestinal motility. The remainder is synthesized in serotonergic neurons of the CNS, where it has various functions. These include the regulation of mood, appetite, and sleep. Serotonin also has some cognitive functions, including memory and learning. Modulation of serotonin at synapses is thought to be a major action of several classes of pharmacological antidepressants.
...
Wikipedia
