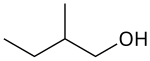
2-methyl-1-butanol
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
2-Methylbutan-1-ol
|
|
| Other names
2-Methyl-1-butanol
Active amyl alcohol |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.809 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C5H12O | |
| Molar mass | 88.148 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.8152 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −117.2 °C (−179.0 °F; 156.0 K) |
| Boiling point | 127.5 °C (261.5 °F; 400.6 K) |
| 31 g/L | |
| Solubility | miscible with ethanol, diethyl ether; very soluble in acetone |
| Vapor pressure | 3 mm Hg |
| Viscosity | 4.453 mPa·s |
| Thermochemistry | |
|
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH |
-356.6 kJ·mol−1 (liquid) -301.4 kJ·mol−1 (gas) |
| Hazards | |
| 385 °C (725 °F; 658 K) | |
| Related compounds | |
|
Related compounds
|
Amyl alcohol |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
2-Methyl-1-butanol (IUPAC name, also called active amyl alcohol) is an organic chemical compound.
It is one of the components of the aroma of Tuber melanosporum, the black truffle.
It is used as a solvent and an intermediate in the manufacture of other chemicals. 2-Methyl-1-butanol is a component of many mixtures of amyl alcohols sold industrially.
2-Methyl-1-butanol can be derived from fusel oil (because it occurs naturally in fruits such as grapes) or manufactured by either the oxo process or via the halogenation of pentane.
...
Wikipedia
