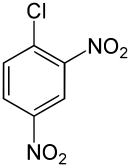
2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
1-Chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene
|
|
| Other names
Dinitrochlorobenzene
Chlorodinitrobenzene 2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene 2,4-Dinitrophenyl chloride 4-Chloro-1,3-dinitrobenzene |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | CDNB; DNCB |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.321 |
| EC Number | 202-551-4 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C6H3ClN2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 202.55 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | yellow crystals |
| Odor | almond-like |
| Density | 1.6867 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 54 °C (129 °F; 327 K) |
| Boiling point | 315 °C (599 °F; 588 K) |
| Insoluble | |
| Solubility | soluble in ether, benzene, CS2 |
|
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.5857 (60 °C) |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Explosive limits | 2-22% |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
1.07 g/kg (rat, oral) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB) is an organic compound with the formula (O2N)2C6H3Cl. It is a yellow solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is an important intermediate for the industrial production of other compounds.
DNCB is produced commercially by the nitration of p-nitrochlorobenzene with a mixture of nitric and sulfuric acids. Other methods afford the compound less efficiently include the chlorination of dinitrobenzene, nitration of o-nitrochlorobenzene and the dinitration of chlorobenzene.
By virtue of the two nitro groups, the chloride is susceptible to nucleophilic substitution. In this way, the compound is a precursor to many other compounds. Base gives the dinitrophenol, ammonia the dinitroaniline, methoxide the dinitroanisole, and amines the secondary amines.
DNCB is used as a substrate in GST enzyme activity assays. The molecule is conjugated to a single molecule of reduced glutathione which then absorbs at 340 nm. Affinity of CDNB for each class of GST varies and so it is not a good measure of activity for some forms (e.g. GSTT and GSTZ).
DNCB can be used to treat warts with an effective cure rate of 80%. DNCB induces an allergic immune response toward the wart-causing virus.
DNCB induces a type IV hypersensitivity reaction in almost all people exposed to it, so it is used medically to assess the T cell activity in patients. This is a useful diagnostic test for immunocompromised patients. It can also be used to treat warts.
DNCB can cause contact dermatitis.
...
Wikipedia

