1917 Atlantic hurricane season
| 1917 Atlantic hurricane season | |
|---|---|
Season summary map
|
|
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | July 6, 1917 |
| Last system dissipated | October 20, 1917 |
| Strongest storm | |
| Name | "Nueva Gerona" |
| • Maximum winds | 150 mph (240 km/h) |
| • Lowest pressure | 928 mbar (hPa; 27.4 inHg) |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 9 |
| Total storms | 4 |
| Hurricanes | 2 |
| Major hurricanes (Cat. 3+) |
2 |
| Total fatalities | 47 total |
| Total damage | $170,000 (1917 USD) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 6 – July 14 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min) <1006 mbar (hPa) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 6 – August 10 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 70 mph (110 km/h) (1-min) <994 mbar (hPa) |
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 30 – September 5 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 120 mph (195 km/h) (1-min) <980 mbar (hPa) |
| Category 4 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 20 – September 30 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 150 mph (240 km/h) (1-min) 928 mbar (hPa) |
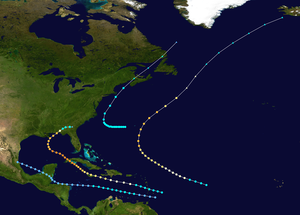
The 1917 Atlantic hurricane season featured nine known tropical cyclones, four of which made landfall. The first system appeared on July 6 east of the Windward Islands. After crossing the islands and traversing the Caribbean Sea, the storm struck Honduras, Belize, and Mexico, before dissipating on July 14. After more than three weeks without tropical cyclogenesis, another tropical storm developed west of Bermuda. As the storm brushed eastern New England, four ships sank near Nantucket, causing 41 fatalities. The same cyclone brought damaging winds to Nova Scotia before transitioning into an extratropical cyclone on August 10.
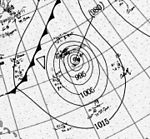
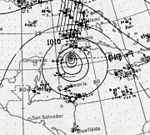
A hurricane developed over the central Atlantic Ocean on August 30 and ultimately affected Bermuda with heightened tides as it passed to the east. Elsewhere, the hurricane had little impact, becoming extratropical on September 5. After the third system, a series of four tropical depressions formed, but failed to become severe. The fourth hurricane brought devastation to Jamaica, Cuba, and portions of the Gulf Coast of the United States, especially western parts of the Florida Panhandle. Overall, the storm left six deaths and inflicted at least $170,000 (1917 USD) in damage.
The season's activity can be quantified in an accumulated cyclone energy (ACE) rating of 61. ACE is, broadly speaking, a measure of the power of the hurricane multiplied by the length of time it existed; therefore, storms that last a long time, as well as particularly strong hurricanes, have high ACE ratings.
...
Wikipedia