1869 Atlantic hurricane season
| 1869 Atlantic hurricane season | |
|---|---|
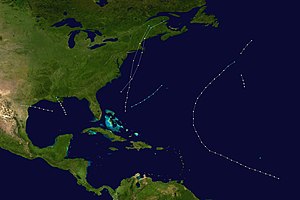
Season summary map
|
|
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | August 12, 1869 |
| Last system dissipated | October 5, 1869 |
| Strongest storm | |
| Name | Six |
| • Maximum winds | 115 mph (185 km/h) (1-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure | 950 mbar (hPa; 28.05 inHg) |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total storms | 10 |
| Hurricanes | 7 |
| Major hurricanes (Cat. 3+) |
1 |
| Total fatalities | 38 |
| Total damage | Unknown |
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 12 – August 12 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 105 mph (165 km/h) (1-min) |
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 16 – August 17 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 105 mph (165 km/h) (1-min) 969 mbar (hPa) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 1 – September 2 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 70 mph (110 km/h) (1-min) |
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 4 – September 6 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 80 mph (130 km/h) (1-min) 985 mbar (hPa) |
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 7 – September 9 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 115 mph (185 km/h) (1-min) 950 mbar (hPa) |
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 11 – September 18 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 105 mph (165 km/h) (1-min) 979 mbar (hPa) |
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 4 – October 5 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 105 mph (165 km/h) (1-min) 965 mbar (hPa) |
The 1869 Atlantic hurricane season was the earliest season in the Atlantic hurricane database in which there were at least ten tropical cyclones. Initially there were only three known storms in the year, but additional research uncovered the additional storms. Meteorologist Christopher Landsea estimates up to six storms may remain missing from the official database for each season in this era, due to small tropical cyclone size, sparse ship reports, and relatively unpopulated coastlines. All activity occurred in a three-month period between the middle of August and early October.
Out of the ten tropical storms, seven reached hurricane intensity, of which four made landfall on the United States. The strongest hurricane was a Category 3 on the modern-day Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale which struck New England at that intensity, one of four storms to do so. It left heavy damage, killing at least one person. The most notable hurricane of the season was the Saxby Gale, which was predicted nearly a year in advance. The hurricane was one of six to produce hurricane-force winds in Maine, where it left heavy damage and flooding. The Saxby Gale left 37 deaths along its path, with its destruction greatest along the Bay of Fundy; there, the hurricane produced a 70.9 ft (21.6 m) high tide near the head of the bay.
The first tropical cyclone of the season was observed on August 12, about 500 mi (800 km) southeast of Cape Race, Newfoundland. Its entire track was unknown, and its existence was only confirmed for 24 hours, based on three ship reports. The second, a barque, the Prinze Frederik Carl, sustained damage to all of its sails. The Hurricane Research Division (HRD) assessed the storm to have moved northeastward in its limited duration, and based on the ship reports estimated peak winds of 105 mph (165 km/h); this would make it a Category 2 hurricane on the modern-day Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale.
...
Wikipedia