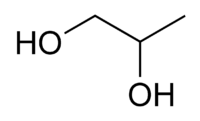
1,2-propanediol
 |
|||
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
Propane-1,2-diol
|
|||
| Other names
Propylene glycol
α-Propylene glycol 1,2-Propanediol 1,2-Dihydroxypropane Methyl ethyl glycol (MEG) Methylethylene glycol |
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.307 | ||
| EC Number | 200-338-0 | ||
| E number | E490 (thickeners, ...) | ||
|
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number | TY6300000 | ||
| UNII | |||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C3H8O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 76.10 g·mol−1 | ||
| Density | 1.036 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −59 °C (−74 °F; 214 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 188.2 °C (370.8 °F; 461.3 K) | ||
| Miscible | |||
| Solubility in ethanol | Miscible | ||
| Solubility in diethyl ether | Miscible | ||
| Solubility in acetone | Miscible | ||
| Solubility in chloroform | Miscible | ||
| Thermal conductivity | 0.34 W/m-K (50% H2O @ 90 °C (194 °F)) | ||
| Viscosity | 0.042 Pa·s | ||
| Pharmacology | |||
| QA16QA01 (WHO) | |||
| Hazards | |||
| S-phrases | S24 S25 | ||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| Related compounds | |||
|
Related glycols
|
Ethylene glycol, 1,3-propanediol | ||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
Propylene glycol, also called propane-1,2-diol, is a synthetic organic compound with the chemical formula C3H8O2. It is a viscous colorless liquid which is nearly odorless but possesses a faintly sweet taste. Chemically it is classed as a diol and is miscible with a broad range of solvents, including water, acetone, and chloroform.
It is produced on a large scale and is primarily used in the production of polymers, but also sees use in food processing, and as a process fluid in low temperature heat exchange applications. In the European Union, it has the E-number E1520 for food applications.
The compound is sometimes called α-propylene glycol to distinguish it from the isomer propane-1,3-diol (β-propylene glycol).
Propylene glycol is a clear, colorless and hygroscopic liquid. Propylene glycol contains an asymmetrical carbon atom, so it exists in two enantiomers. The commercial product is a racemic mixture. Pure optical isomers can be obtained by hydration of optically pure propylene oxide.
The freezing point of water is depressed when mixed with propylene glycol owing to the effects of dissolution of a solute in a solvent (freezing-point depression). In general, glycols are non-corrosive, have very low volatility and very low toxicity; however, the closely related ethylene glycol (a key ingredient in antifreeze) is extremely toxic to humans and fatally toxic to many animals.
Industrially, propylene glycol is produced from propylene oxide (for food-grade use), and global capacity in 1990 was 900,000 tonnes per year. Different manufacturers use either non-catalytic high-temperature process at 200 °C (392 °F) to 220 °C (428 °F), or a catalytic method, which proceeds at 150 °C (302 °F) to 180 °C (356 °F) in the presence of ion exchange resin or a small amount of sulfuric acid or alkali.
...
Wikipedia



