Γ-hydroxybutyric acid
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Usually by mouth; intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 25% (oral) |
| Metabolism | 95%, mainly liver, also in blood and tissues |
| Onset of action | Within 5–15 min |
| Biological half-life | 30–60 minutes |
| Excretion | 5%, kidney |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| Synonyms | γ-Hydroxybutyric acid γ-Hydroxybutyrate GHB |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
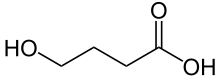
| Formula | C4H8O3 |
| Molar mass | 104.10 g/mol (GHB) 126.09 g/mol (sodium salt) 142.19 g/mol (potassium salt) |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
γ-Hydroxybutyric acid (GHB), also known as 4-hydroxybutanoic acid, is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter and a psychoactive drug. It is a precursor to GABA, glutamate, and glycine in certain brain areas, and it acts on the GHB receptor and it is a weak agonist at the GABAB receptor.
GHB has been used in a medical setting as a general anesthetic and as a treatment for cataplexy, narcolepsy, and alcoholism. It is also used illegally as an intoxicant, to try to increase athletic performance, and as a date rape drug. It is commonly used in the form of a salt, such as sodium γ-hydroxybutyrate (Na.GHB, sodium oxybate, or Xyrem) or potassium γ-hydroxybutyrate (K.GHB, potassium oxybate).
GHB is also produced as a result of fermentation, and is found in small quantities in some beers and wines, beef and small citrus fruits.
Succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency is a disease that causes GHB to accumulate in the blood.
The only common medical use for GHB today are in the treatment of narcolepsy and more rarely alcoholism. It is sometimes used off-label for the treatment of fibromyalgia.
GHB is the active ingredient in the prescription medication sodium oxybate (Xyrem). Sodium oxybate is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of cataplexy associated with narcolepsy and excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS) associated with narcolepsy.
...
Wikipedia
