Sodium oxybate
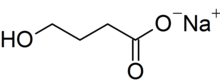 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Xyrem, Alcover |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a605032 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| ATC code | N07XX04 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 88% |
| Protein binding | <1% |
| Biological half-life | 0.5 to 1 hour. |
| Excretion | Almost entirely by biotransformation to carbon dioxide, which is then eliminated by expiration |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| Synonyms | NSC-84223, WY-3478 |
| CAS Number |
502-85-2 |
| PubChem (CID) | 23663870 |
| ChemSpider |
9983 |
| UNII |
7G33012534 |
| KEGG |
D05866 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL1200682 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.231 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C4H7NaO3 |
| Molar mass | 126.09 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sodium oxybate (USAN) (brand names Xyrem, Alcover, Anetamin, Gamanest, Gioron, Somsanit), contracted from sodium γ-hydroxybutyrate, is a prescription medication approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS) associated with narcolepsy, and by the FDA, Health Canada and in some areas of the United Kingdom National Health Service for the treatment of cataplexy associated with narcolepsy. Sodium oxybate is the sodium salt of γ-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB). Xyrem is manufactured by Jazz Pharmaceuticals in the US and Valeant Pharmaceuticals in Canada. Under the name Alcover, it is used in Italy for treatment of alcohol withdrawal and dependence.
The American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM) recommends sodium oxybate as a standard of care for the treatment of cataplexy, daytime sleepiness, and disrupted sleep due to narcolepsy in its Practice Parameters for the Treatment of Narcolepsy and other Hypersomnias of Central Origin, and the drug has been safely used by patients with narcolepsy since 2002. A recent analysis evaluated the postmarketing safety of sodium oxybate, including rates of abuse, dependence, and withdrawal, using a conservative application of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th Edition (DSM-IV) criteria to all worldwide sodium oxybate adverse event cases containing reporting terminology related to abuse or misuse. The analysis included cases reported to the manufacture from market introduction in 2002 through March 2008. Using the DSM-IV criteria, the analysis found the following rates of abuse, dependence, and withdrawal of the approximately 26,000 patients who used sodium oxybate during this period:
...
Wikipedia
