Łódź Voivodeship (1919-1939)
| Łódź Voivodeship Województwo łódzkie |
|||||
| Voivodeship of Poland | |||||
|
|||||
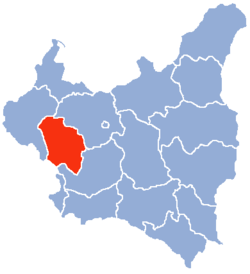
| Łódź Voivodeship (red) on the map of Second Polish Republic | |||||
| Capital | Łódź | ||||
| Government | Voivodeship | ||||
| Voivodes | |||||
| • | 1919-1922 | Antoni Kamieński | |||
| • | 1938-1939 | Henryk Józewski | |||
| Historical era | Interwar period | ||||
| • | Established | 14 August 1919 | |||
| • | Territorial changes | 1 April 1938 | |||
| • | Annexed | September 1939 | |||
| Area | |||||
| • | 1921 | 19,034 km2(7,349 sq mi) | |||
| • | 1939 | 20,446 km2(7,894 sq mi) | |||
| Population | |||||
| • | 1921 | 2,252,769 | |||
| Density | 118.4 /km2 (306.5 /sq mi) | ||||
| • | 1931 | 2,650,100 | |||
| Political subdivisions | 15 powiats (1939) | ||||
Łódź Voivodeship (Polish: Wojewodztwo Łódzkie) was a unit of administrative division and local government in Poland in years 1919–1939. At that time, it covered a large portion of the mid-western part of the country, including such cities as Łódź, Piotrków Trybunalski, Sieradz and Radomsko. The capital of the Łódź Voivodeship was always Łódź, but the area of land which comprised it changed several times.
In early 1939, the Voivodeship's area was 20,446 square kilometers. It was located in middle Poland, bordering Poznań Voivodeship to the west, Pomorze Voivodeship to the north, Warsaw Voivodeship to the east Kielce Voivodeship to the south and Germany to the southwest. Landscape was flat, forests covered only 14.7%, with the national average 22.2% (as of January 1, 1937).
In 1938 some western counties were ceded to Poznań Voivodeship (see: Territorial changes of Polish Voivodeships on April 1, 1938). After the change, it consisted of 15 powiats (counties):
...
Wikipedia