Wenckebach
| Second-degree atrioventricular block | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Cardiology |
| ICD-10 | I44.1 |
| ICD-9-CM | 426.12, 426.13 |
| DiseasesDB | 10477 |
| eMedicine | emerg/234 |
Second-degree atrioventricular block (AV block) is a disease of the electrical conduction system of the heart. It is a conduction block between the atria and ventricles.
The presence of second-degree AV block is diagnosed when one or more (but not all) of the atrial impulses fail to conduct to the ventricles due to impaired conduction.
Most people with Wenckebach (Type I Mobitz) do not show symptoms. However, those that do usually display one or more of the following:
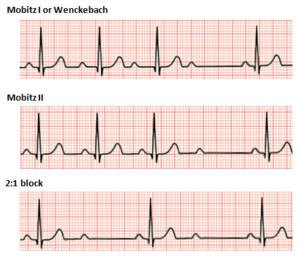
There are two non-distinct types of second-degree AV block, called Type 1 and Type 2. In both types, a P wave is blocked from initiating a QRS complex; but, in Type 1, there are increasing delays in each cycle before the omission, whereas, in Type 2, there is no such pattern.
Type 1 second-degree heart block is considered a more benign entity than type 2 second-degree heart block.
Both types are named after Woldemar Mobitz. Type I is also named for Karel Frederik Wenckebach, and type II is also named for John Hay.
Type 1 Second-degree AV block, also known as Mobitz I or Wenckebach periodicity, is almost always a disease of the AV node.
Mobitz I heart block is characterized by progressive prolongation of the PR interval on the electrocardiogram (ECG) on consecutive beats followed by a blocked P wave (i.e., a 'dropped' QRS complex). After the dropped QRS complex, the PR interval resets and the cycle repeats.
One of the baseline assumptions when determining if an individual has Mobitz I heart block is that the atrial rhythm has to be regular. If the atrial rhythm is not regular, there could be alternative explanations as to why certain P waves do not conduct to the ventricles.
This is almost always a benign condition for which no specific treatment is needed. In symptomatic cases, intravenous atropine or isoproterenol may transiently improve conduction.
...
Wikipedia
