Vinorelbine
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Navelbine |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a695013 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
intravenous, by mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 43 ± 14% (oral) |
| Protein binding | 79 to 91% |
| Metabolism | liver (CYP3A4-mediated) |
| Biological half-life | 27.7 to 43.6 hours |
| Excretion | Fecal (46%) and kidney (18%) |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
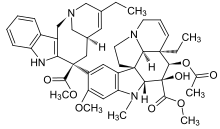
| Formula | C45H54N4O8 |
| Molar mass | 778.932 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vinorelbine (NVB), sold under the brand name Navelbine among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes breast cancer and non-small cell lung cancer. It is given by injection into a vein or by mouth.
Common side effects include bone marrow suppression, pain at the site of injection, vomiting, feeling tired, numbness, and diarrhea. Other serious side effects include shortness of breath. Use during pregnancy may harm the baby. Vinorelbine is in the vinca alkaloid family of medications. It is believed to work by disrupting the normal function of microtubules and thereby stopping cell division.
Vinorelbine was approved for medical use in the United States in 1994. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system. The wholesale price in the developing world as of 2014 is between 18.10 and 42.82 USD per 50 mg vial. This amount in the United Kingdom costs the NHS about 139.00 pounds.
Vinorelbine is approved for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. It is used off-label for other cancers such as metastatic breast cancer. It is also active in rhabdomyosarcoma.
Vinorelbine has a number of side-effects that can limit its use:
Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (a progressive, enduring and often irreversible tingling numbness, intense pain, and hypersensitivity to cold, beginning in the hands and feet and sometimes involving the arms and legs), lowered resistance to infection, bruising or bleeding, anaemia, constipation, vomitings, diarrhea, nausea, tiredness and a general feeling of weakness (asthenia), inflammation of the vein into which it was injected (phlebitis). Seldom severe hyponatremia is seen.
...
Wikipedia
