Thiomersal
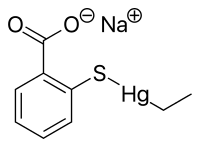 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Ethyl(2-mercaptobenzoato-(2-)-O,S) mercurate(1-) sodium
|
|
| Other names
Mercury((o-carboxyphenyl)thio)ethyl sodium salt
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
54-64-8 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:9546 |
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL508338 |
| ChemSpider |
10772045 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.192 |
| EC Number | 200-210-4 |
| PubChem | 16684434 |
| RTECS number | OV8400000 |
| UNII |
2225PI3MOV |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C9H9HgNaO2S | |
| Molar mass | 404.81 g/mol |
| Appearance | White or slightly yellow powder |
| Density | 2.508 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 232 to 233 °C (450 to 451 °F; 505 to 506 K) (decomposition) |
| 1000 g/l (20 °C) | |
| Pharmacology | |
| D08AK06 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
|
EU classification (DSD)
|
Very toxic (T+) Dangerous for the environment (N) Repr. Cat. 1 |
| R-phrases | R26/27/28 R33 R40 R50/53 R60 R61 |
| S-phrases | S13 S28 S36 S45 S53 S60 S61 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | 250 °C (482 °F; 523 K) |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
75 mg/kg (oral, rat) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Thiomersal (INN), or thimerosal (USP), is an organomercury compound. This compound is a well established antiseptic and antifungal agent.
The pharmaceutical corporation Eli Lilly and Company gave thiomersal the trade name Merthiolate. It has been used as a preservative in vaccines, immunoglobulin preparations, skin test antigens, antivenins, ophthalmic and nasal products, and tattoo inks. Its use as a vaccine preservative was controversial, and it was phased out from routine childhood vaccines in the European Union, and a few other countries in response to popular fears. The current scientific consensus is that no convincing scientific evidence supports these fears.
In the U.S., Thiomersal has been removed from or reduced to trace amounts in all vaccines routinely recommended for children 6 years of age and younger with the exception of inactivated influenza vaccine. Vaccines with trace amounts of thiomersal contain 1 microgram or less of mercury per dose.
Morris Kharasch, a chemist at the University of Maryland, filed a patent application for thiomersal in 1927; Eli Lilly later marketed the compound under the trade name Merthiolate.In vitro tests conducted by Lilly investigators H. M. Powell and W. A. Jamieson found that it was forty to fifty times as effective as phenol against Staphylococcus aureus. It was used to kill bacteria and prevent contamination in antiseptic ointments, creams, jellies, and sprays used by consumers and in hospitals, including nasal sprays, eye drops, contact lens solutions, immunoglobulins, and vaccines. Thiomersal was used as a preservative (bactericide) so that multidose vials of vaccines could be used instead of single-dose vials, which are more expensive. By 1938, Lilly's assistant director of research listed thiomersal as one of the five most important drugs ever developed by the company.
...
Wikipedia

