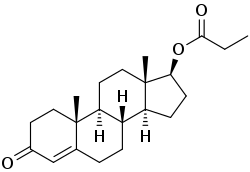
Testosterone propionate
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Agrovirin, Andronate, Andrusol-P, Masenate, Neo-Hombreol, Oreton, Perandren, Synandrol, Testoviron, numerous others |
| Routes of administration |
Intramuscular injection |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| Synonyms | NSC-9166 |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H32O3 |
| Molar mass | 344.50 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Testosterone propionate (USAN, BAN) (brand names Agrovirin, Andronate, Andrusol-P, Masenate, Neo-Hombreol, Oreton, Perandren, Synandrol, Testoviron, numerous others), or testosterone propanoate, also known as propionyltestosterone, is an androgen and anabolic steroid and a testosterone ester. Testosterone esters were synthesized for the first time in 1936, and were found to have greatly improved potency relative to testosterone. Among the esters synthesized, testosterone propionate was the most potent, and for this reason, was selected for further development, subsequently being marketed. Along with testosterone enanthate, testosterone cypionate, and testosterone undecanoate, testosterone propionate is one of the most widely used testosterone esters.
Testosterone propionate was introduced in 1937 by Schering AG in Germany under the brand name Testoviron. It was the first ester of testosterone to be introduced, and was the major form of testosterone used medically before 1960. In the 1950s, longer-acting testosterone esters like testosterone enanthate and testosterone cypionate were introduced and superseded testosterone propionate. Although rarely used nowadays due to its short duration, testosterone propionate remains medically available and is still marketed in the United States.
...
Wikipedia
