Stink damp
 |
|||
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Systematic IUPAC name
Hydrogen sulfide
|
|||
Other names
|
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|||
| 3DMet | B01206 | ||
| 3535004 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.070 | ||
| EC Number | 231-977-3 | ||
| 303 | |||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | Hydrogen+sulfide | ||
|
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number | MX1225000 | ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1053 | ||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| H2S | |||
| Molar mass | 34.08 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless gas | ||
| Odor | Rotten eggs | ||
| Density | 1.363 g dm−3 | ||
| Melting point | −82 °C (−116 °F; 191 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −60 °C (−76 °F; 213 K) | ||
| 4 g dm−3 (at 20 °C) | |||
| Vapor pressure | 1740 kPa (at 21 °C) | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 7.0 | ||
| Basicity (pKb) | 12.9 | ||
| −25.5·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
|
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.000644 (0 °C) | ||
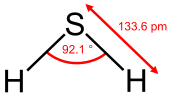
| Structure | |||
| C2v | |||
| Bent | |||
| 0.97 D | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
| 1.003 J K−1 g−1 | |||
|
Std molar
entropy (S |
206 J mol−1 K−1 | ||
|
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH |
−21 kJ mol−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS | ||
|
EU classification (DSD)
|
|
||
| R-phrases | R12, R26, R50 | ||
| S-phrases | (S1/2), S9, S16, S36, S38, S45, S61 | ||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| Flash point | −82.4 °C (−116.3 °F; 190.8 K) | ||
| 232 °C (450 °F; 505 K) | |||
| Explosive limits | 4.3–46% | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
|
LC50 (median concentration)
|
|
||
|
LCLo (lowest published)
|
|
||
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |||
|
PEL (Permissible)
|
C 20 ppm; 50 ppm [10-minute maximum peak] | ||
|
REL (Recommended)
|
C 10 ppm (15 mg/m3) [10-minute] | ||
|
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
100 ppm | ||
| Related compounds | |||
|
Related hydrogen chalcogenides
|
|||
|
Related compounds
|
Phosphine | ||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
Hydrogen sulfide is the chemical compound with the formula H
2S. It is a colorless gas with the characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. It is very poisonous, corrosive, and flammable.
Hydrogen sulfide often results from the microbial breakdown of organic matter in the absence of oxygen gas, such as in swamps and sewers; this process is commonly known as anaerobic digestion. H
2S also occurs in volcanic gases, natural gas, and in some sources of well water. The human body produces small amounts of H
2S and uses it as a signaling molecule.
Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele is credited with having discovered hydrogen sulfide in 1777.
The British English spelling of this compound is hydrogen sulphide, but this spelling is not recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry or the Royal Society of Chemistry.
Hydrogen sulfide is slightly heavier than air; a mixture of H
2S and air can be explosive. Hydrogen sulfide and oxygen burn with a blue flame to form sulfur dioxide (SO
2) and water. In general, hydrogen sulfide acts as a reducing agent, especially in the presence of base, which forms SH−.
...
Wikipedia



