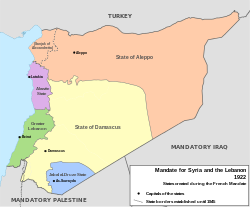
State of Damascus
| State of Damascus | ||||||||||
|
État de Damas دولة دمشق |
||||||||||
| Mandate of France | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Location of the State of Damascus (yellow)
within the Mandate for Syria. |
||||||||||
| Capital | Damascus | |||||||||
| Languages |
French Arabic |
|||||||||
| Political structure | League of Nations Mandate | |||||||||
| Historical era | Interwar period | |||||||||
| • | Mandate granted | 3 September 1920 | ||||||||
| • | Federation established | 22 June 1922 | ||||||||
| • | Unification of Aleppo and Damascus | 1 December 1924 | ||||||||
|
||||||||||
The State of Damascus (1920–1924; French: État de Damas; Arabic: دولة دمشق Dawlat Dimashq ) was one of the six states established by the French General Henri Gouraud in the French Mandate of Syria which followed the San Remo conference and the defeat of King Faisal's short-lived monarchy in Syria.
The other states were the State of Aleppo (1920), the State of Alawites (1920), the State of Jabal Druze (1921), and The Sanjak of Alexandretta (1921). The State of Greater Lebanon (1920) became later the modern country of Lebanon.
The State of Damascus was declared by the French General Henri Gouraud on 3 September 1920, with Damascus as its capital. The first president of the new state was Haqqi Al-Azm. The state of Damascus included Damascus and its surrounding region, in addition to the cities of Homs, Hama and the Orontes river valley.
...
Wikipedia