Silver sulfate
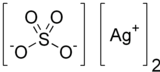 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Silver sulfate
|
|
| Other names
disilver(1+) salt
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.581 |
| EC Number | 233-653-7 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3077 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| Ag2SO4 | |
| Appearance | Colorless crystals |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 5.45 g/cm3 (25 °C) 4.84 g/cm3 (660 °C) |
| Melting point | 652.2–660 °C (1,206.0–1,220.0 °F; 925.4–933.1 K) |
| Boiling point | 1,085 °C (1,985 °F; 1,358 K) |
| 0.57 g/100 mL (0 °C) 0.69 g/100 mL (10 °C) 0.83 g/100 mL (25 °C) 0.96 g/100 mL (40 °C) 1.33 g/100 mL (100 °C) |
|
|
Solubility product (Ksp)
|
1.2·10−5 |
| Solubility | Dissolves in aq. acids, alcohols, acetone, ether, acetates, amides Insoluble in ethanol |
| Solubility in sulfuric acid | 8.4498 g/L (0.1 molH2SO4/LH2O) 25.44 g/100 g (13 °C) 31.56 g/100 g (24.5 °C) 127.01 g/100 g (96 °C) |
| Solubility in ethanol | 7.109 g/L (0.5 nEtOH/H2O) |
| Solubility in acetic acid | 7.857 g/L (0.5 nAcOH/H2O) |
| −9.29·10−5 cm3/mol | |
|
Refractive index (nD)
|
nα = 1.756 nβ = 1.775 nγ = 1.782 |
| Structure | |
| Orthorhombic, oF56 | |
| Fddd, No. 70 | |
| 2/m 2/m 2/m | |
|
a = 10.2699(5) Å, b = 12.7069(7) Å, c = 5.8181(3) Å
α = 90°, β = 90°, γ = 90°
|
|
| Thermochemistry | |
| 131.4 J/mol·K | |
|
Std molar
entropy (S |
200.4 kJ/mol |
|
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH |
−715.9 kJ/mol |
|
Gibbs free energy (ΔfG˚)
|
−618.4 J/mol·K |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |
 
|
| GHS signal word | Danger |
| H318, H410 | |
| P273, P280, P305+351+338, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 | |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Silver sulfate (Ag2SO4) is an ionic compound of silver used in silver plating and as a non-staining substitute to silver nitrate. This sulfate is stable under ordinary conditions of use and storage, though it darkens upon exposure to air or light. It is minimally soluble in water.
Silver sulfate is prepared by adding sulfuric acid to a solution of silver nitrate:
AgNO3(aq) + H2SO4(aq) = AgHSO4(aq) + HNO3(aq)
2 AgHSO4(aq) <=> Ag2SO4(s) + H2SO4(aq) reversible reaction
The precipitate is then washed with hot water and preparation is under ruby red illumination.
The synthesis of silver(II) sulfate (AgSO4) with a divalent silver ion instead of a monovalent silver ion was first reported in 2010 by adding sulfuric acid to silver(II) fluoride (HF escapes). It is a black solid that decomposes exothermally at 120 °C with evolution of oxygen and the formation of the pyrosulfate.
...
Wikipedia

