Sesklo
|
Sesklo Σέσκλο |
|
|---|---|
| Coordinates: 39°21.3′N 22°50.1′E / 39.3550°N 22.8350°ECoordinates: 39°21.3′N 22°50.1′E / 39.3550°N 22.8350°E | |
| Country | Greece |
| Administrative region | Thessaly |
| Regional unit | Magnesia |
| Municipality | Volos |
| Municipal unit | Aisonia |
| Elevation | 200 m (700 ft) |
| Community | |
| • Population | 970 (2011) |
| Time zone | EET (UTC+2) |
| • Summer (DST) | EEST (UTC+3) |
| Postal code | 385 00 |
| Area code(s) | 24210 |
 |
|
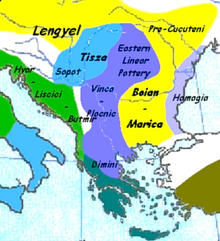
| Alternative names | Map showing the main cultures of Neolithic Greece c. 7000 BC — c. 3200 BC |
|---|---|
| Geographical range | Eastern Europe |
| Period | Neolithic Greece |
| Dates | c. 6850 BC — c. 4400 BC |
| Type site | Sesklo |
| Major sites | Sesklo |
| Preceded by | Neolithic Greece |
| Followed by | Dimini culture, Starčevo–Kőrös–Criș culture |
Sesklo (Greek: Σέσκλο) is a village near the city of Volos. Volos is located within the municipality of Aisonia. Aisonia is located within the regional unit of Magnesia. Magnesia is located within the administrative region of Thessaly. Thessaly is located within Greece.
This settlement gives its name to the first Neolithic culture of Europe, which inhabited Thessaly and parts of Macedonia. The Neolithic settlement was discovered in the 1800s and the first excavations were made by Greek archaeologist, Christos Tsountas. The oldest fragments researched at Sesklo place the civilization's development as far back as c. 7510 BC — c. 6190 BC, known as proto-Sesklo and pre-Sesklo and they show an advanced agriculture and a very early use of pottery that rivals in age those of the near east. Available data also indicates that domestication of cattle occurred at Argissa as early as c. 6300 BC during the Pre-Pottery Neolithic.
The aceramic levels at Sesklo contained bone fragments of domesticated cattle too. The earliest occurrence reported in the near east is at Çatalhöyük, in stratum VI, dating c. 5750 BC, though it might have been present in stratum XII too — c. 6100 BC. The Neolithic settlement was covering an area of about 20 hectares in its peak period c. 5000 BC and comprised about 500 — 800 houses with a population of perhaps up to 5,000 people.
...
Wikipedia

