Neolithic Greece
 |
|
| Period | Neolithic Europe |
|---|---|
| Dates | c. 7000 – c. 3200 BC |
| Major sites | Nea Nikomedeia, Sesklo, Dimini, Franchthi Cave, Athens |
| Preceded by | Balkan Mesolithic, Pre-Pottery Neolithic B |
| Followed by | Sesklo culture, Cycladic culture, Minoan civilization, Helladic period, Cardium Pottery, Starčevo culture |
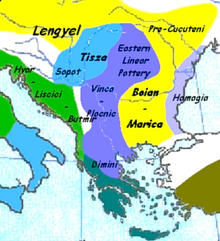
Neolithic Greece is an archaeological term used to refer to the Neolithic phase of Greek history beginning with the spread of farming to Greece in 7000–6500 BC. During this period, many developments occurred such as the establishment and expansion of a mixed farming and stock-rearing economy, architectural innovations (i.e. "megaron-type" and "Tsangli-type" houses), as well as elaborate art and tool manufacturing.
The Neolithic Revolution reached Europe beginning in 7000–6500 BC when agriculturalists from the Near East entered the Greek peninsula from Anatolia mainly by island-hopping through the Aegean Sea. Modern archaeologists have divided the Neolithic period of Greek history into six phases: Pre-Pottery, Early Neolithic, Middle Neolithic, Late Neolithic I, Late Neolithic II and Final Neolithic (or Chalcolithic).
These are the estimated populations of hamlets, villages, and towns of Neolithic Greece over time. Note that there are several problems with estimating the sizes of individual settlements, and the highest estimates for a given settlements, in a given period, may be several times the lowest.
The Pre-Ceramic (or Aceramic) period of Neolithic Greece is characterized by the absence of baked clay pots and an economy based on farming and stock-rearing. Settlements consisted of subterranean huts partially dug into the ground with communities inhabited by 50 to 100 people in places such as Argissa (Thessaly), Dendra (Argolid) and Franchthi. The inhabitants cultivated various crops (i.e. einkorn, emmer wheat, barley, lentils and peas), engaged in fishing, hunting, animal husbandry (i.e. raising cattle, pigs, sheep, dogs and goats), developed tools (i.e. blades made from flint and obsidian) and produced jewellery from clay, seashells, bone and stone.
...
Wikipedia
