Sesamum indicum
| Sesamum | |
|---|---|
 |
|
 |
|
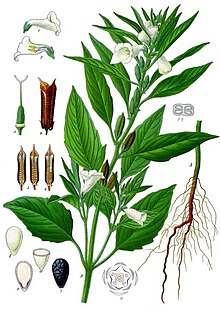
| Sesame plants | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (unranked): | Angiosperms |
| (unranked): | Eudicots |
| (unranked): | Asterids |
| Order: | Lamiales |
| Family: | Pedaliaceae |
| Genus: | Sesamum |
| Species: | S. indicum |
| Binomial name | |
|
Sesamum indicum L. |
|
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Sesame (/ˈsɛsəmiː/; Sesamum indicum) is a flowering plant in the genus Sesamum, also called benne. Numerous wild relatives occur in Africa and a smaller number in India. It is widely naturalized in tropical regions around the world and is cultivated for its edible seeds, which grow in pods or "buns". The world harvested 4.2 million metric tonnes of sesame seeds in 2013, with India and China as the largest producers.
Sesame seed is one of the oldest oilseed crops known, domesticated well over 3000 years ago. Sesame has many species, most being wild and native to sub-Saharan Africa. Sesame indicum, the cultivated type, originated in India and is tolerant to drought-like conditions, growing where other crops fail.
Sesame has one of the highest oil contents of any seed. With a rich, nutty flavor, it is a common ingredient in cuisines across the world. Like other nuts and foods, it can trigger allergic reactions in some people.
Sometimes sold with its seed coat removed (decorticated), this variety is often present on top of baked goods in many countries.
The word "sesame" is from Latin sesamum or Greek sēsamon; it also has derivation from Arabic semsem. From these roots, words with the generalized meaning “oil, liquid fat” were derived.
Sesame names vary among numerous languages.
Sesame seed is considered to be the oldest oilseed crop known to humanity. The genus has many species, and most are wild. Most wild species of the genus Sesamum are native to sub-Saharan Africa. Sesame indicum, the cultivated type, originated in India.
Charred remains of sesame recovered from archeological excavations have been dated to 3500-3050 BC. Fuller claims trading of sesame between Mesopotamia and the Indian sub-continent occurred by 2000 BC. Some reports claim sesame was cultivated in Egypt during the Ptolemiac period, while others suggest the New Kingdom.
...
Wikipedia
