Selenium hexafluoride
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Selenium hexafluoride
|
|||
| Other names
Selenium(VI) fluoride, Selenium fluoride
|
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.149.506 | ||
|
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number | VS9450000 | ||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| SeF6 | |||
| Molar mass | 192.9534 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | colourless gas | ||
| Density | 0.007887 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −34.6 °C (−30.3 °F; 238.6 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −46.6 °C (−51.9 °F; 226.6 K) sublimes | ||
| insoluble | |||
| Vapor pressure | >1 atm (20°C) | ||
| −51.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
|
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.895 | ||
| Structure | |||
| Orthorhombic, oP28 | |||
| Pnma, No. 62 | |||
| octahedral (Oh) | |||
| 0 | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
|
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH |
1030 kJ/mol | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | toxic, corrosive | ||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
|
LCLo (lowest published)
|
10 ppm (rat, 1 hr) 10 ppm (mouse, 1 hr) 10 ppm (guinea pig, 1 hr) |
||
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |||
|
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 0.05 ppm (0.4 mg/m3) | ||
|
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 0.05 ppm | ||
|
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
2 ppm | ||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
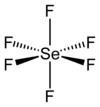
Selenium hexafluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula SeF6. It is a colourless gas described as having a "repulsive" odor. It is not widely encountered and has no commercial applications.
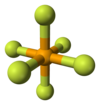
Like many compounds of selenium, SeF6 is hypervalent. The compound has octahedral molecular geometry with an Se−F bond length of 168.8 pm.
SeF6 can be prepared from the elements or by the reaction of bromine trifluoride (BrF3) with selenium dioxide. The crude product is purified by sublimation.
The relative reactivity of the hexafluorides of S, Se, and Te follows the order TeF6 > SeF6 > SF6, the latter being completely inert toward hydrolysis until high temperatures. SeF6 also resists hydrolysis. The gas can be passed through 10% NaOH or KOH without change, but reacts with gaseous ammonia at 200 °C.
Although selenium hexafluoride is quite inert and slow to hydrolyze, it is toxic even at low concentrations, especially by longer exposure. In the U.S., OSHA and ACGIH standards for selenium hexafluoride exposure is an upper limit of 0.05 ppm in air averaged over an eight-hour work shift. Additionally, selenium hexafluoride is designated as IDLH chemical with a maximum allowed exposure limit of 2 ppm.
...
Wikipedia