Scleritis
| Scleritis | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Inflammation of entire thickness of the sclera | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | ophthalmology |
| ICD-10 | H15.0 |
| ICD-9-CM | 379.0 |
| DiseasesDB | 11898 |
| MedlinePlus | 001003 scleritis. 001019 episcleritis |
| eMedicine | emerg/521 oph/642 |
| MeSH | D015423 |
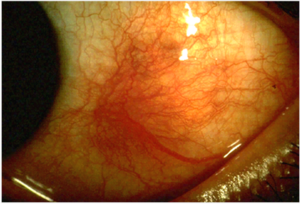
Scleritis is a serious inflammatory disease that affects the white outer coating of the eye, known as the sclera. The disease is often contracted through association with other diseases of the body, such as granulomatosis with polyangiitis or rheumatoid arthritis. There are three types of scleritis: diffuse scleritis (the most common), nodular scleritis, and necrotizing scleritis (the most severe). Scleritis may be the first symptom of onset of connective tissue disease.
Episcleritis is inflammation of the episclera, a less serious condition that seldom develops into scleritis.
Symptoms of scleritis include:
The pain of episcleritis is less severe than in scleritis. In hyperemia, there is a visible increase in the blood flow to the sclera (hyperaemia), which accounts for the redness of the eye. Unlike in conjunctivitis, this redness will not move with gentle pressure to the conjunctiva.
Scleritis can be classified as anterior scleritis and posterior scleritis. Anterior scleritis is the most common variety, accounting for about 98% of the cases. It is of two types : Non-necrotising and necrotising. Non-necrotising scleritis is the most common, and is further classified into diffuse and nodular type based on morphology. Necrotising scleritis accounts for 13% of the cases. It can occur with or without inflammation.
Most of the time, scleritis is not caused by an infectious agent. Histopathological changes are that of a chronic granulomatous disorder, characterized by fibrinoid necrosis, infiltration by polymorphonuclear cells, lymphocytes, plasma cells and macrophages. The granuloma is surrounded by multinucleated epitheloid giant cells and new vessels, some of which may show evidence of vasculitis.
Scleritis is best detected by examining the sclera in daylight; retracting the lids helps determine the extent of involvement. Other aspects of the eye exam (i.e. visual acuity testing, slit lamp examination, etc.) may be normal. Scleritis may be differentiated from episcleritis by using phenylephrine or neosynephrine eye drops, which causes blanching of the blood vessels in episcleritis, but not in scleritis.
...
Wikipedia
