Safinamide
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Xadago |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | UK Drug Information |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 95% |
| Protein binding | 88–90% |
| Metabolism | Amidases, glucuronidation |
| Biological half-life | 20–30 hrs |
| Excretion | 76% renal, 1.5% faeces |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
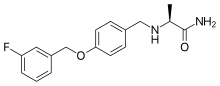
| Synonyms | EMD-1195686, PNU-15774E; (2S)-2-[[4-[(3-fluorophenyl)methoxy]phenyl] methylamino]propanamide |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.120.167 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H19FN2O2 |
| Molar mass | 302.34 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Safinamide (INN; brand name Xadago) is a drug used as an add-on treatment for Parkinson's disease during "off" episodes; it has monoamine oxidase B inhibiting and other methods of action.
It was approved in Europe in February 2015, and in the United States in March 2017.
Safinamide is used to treat idiopathic Parkinson’s disease as add-on for people taking a stable dose of levodopa (L-dopa) alone or in combination with other Parkinson drugs, to help with "off" episodes when levadopa stops working.
Safinamide is contraindicated in people with severe liver impairment, with albinism, retinitis pigmentosa, severe diabetic neuropathy, uveitis and other disorders of the retina. Combination with other monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors and pethidine is also contraindicated.
It is pregnancy category C in the US; it is not safe for women to take during pregnancy. It is excreted in breast milk and the effects are infants are unknown.
Common adverse events in clinical trials (in more than 1% of people) included nausea, dizziness, tiredness, sleeplessness, orthostatic hypotension (low blood pressure), and headache. There was no significant difference in the occurrence of these effects between safinamide and placebo.
In experiments with rats (but not in those with monkeys), retinopathies have been observed.
Expected overdose effects are hypertension (high blood pressure), orthostatic hypotension, hallucinations, psychomotor agitation, nausea, vomiting, and dyskinesia. In studies, a singe person was suspected to have overdosed for a month; symptoms were confusion, drowsiness and mydriasis (dilation of the pupils) and subsided completely after the drug was discontinued. No specific antidote is available.
...
Wikipedia
