SH3 domain
| SH3 domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
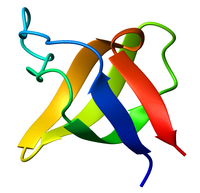
Ribbon diagram of the SH3 domain, alpha spectrin, from chicken (PDB accession code 1SHG), colored from blue (N-terminus) to red (C-terminus).
|
|||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | SH3_1 | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00018 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0010 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR001452 | ||||||||
| SMART | SM00326 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PS50002 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1shf | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 1shf | ||||||||
| CDD | cd00174 | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Available protein structures: | |
|---|---|
| Pfam | structures |
| PDB | RCSB PDB; PDBe; PDBj |
| PDBsum | structure summary |
The SRC Homology 3 Domain (or SH3 domain) is a small protein domain of about 60 amino acid residues. Initially, SH3 was described as a conserved sequence in the viral adaptor protein v-Crk. This domain is also present in the molecules of phospholipase and several cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases such as Abl and Src. It has also been identified in several other protein families such as: PI3 Kinase, Ras GTPase-activating protein, CDC24 and cdc25. SH3 domains are found in proteins of signaling pathways regulating the cytoskeleton, the Ras protein, and the Src kinase and many others. The SH3 proteins interact with adaptor proteins and tyrosine kinases. Interacting with tyrosine kinases SH3 proteins usually bind far away from the active site. Approximately 300 SH3 domains are found in proteins encoded in the human genome. In addition to that, the SH3 domain was responsible for controlling protein-protein interactions in the signal transduction pathways and regulating the interactions of proteins involved in the cytoplasmic signaling.
The SH3 domain has a characteristic beta-barrel fold that consists of five or six β-strands arranged as two tightly packed anti-parallel β sheets. The linker regions may contain short helices. The SH3-type fold is an ancient fold found in eukaryotes as well as prokaryotes.
The classical SH3 domain is usually found in proteins that interact with other proteins and mediate assembly of specific protein complexes, typically via binding to proline-rich peptides in their respective binding partner. Classical SH3 domains are restricted in humans to intracellular proteins, although the small human MIA family of extracellular proteins also contain a domain with an SH3-like fold.
...
Wikipedia
