Romanian-language
| Romanian | |
|---|---|
| Daco-Romanian | |
| limba română | |
| Pronunciation | [roˈmɨnə] |
| Native to | Romania, Moldova, Transnistria (disputed region); minority in Israel, Serbia, Ukraine, Hungary, Croatia, Bulgaria; diaspora in Italy, Spain, Germany and other parts of Western Europe |
|
Native speakers
|
24-26 million (2004–2012) Second language: 4 million |
|
Indo-European
|
|
|
Early form
|
|
|
Latin (Romanian alphabet) Cyrillic (Transnistria only) Romanian Braille |
|
| Official status | |
|
Official language in
|
Romania Moldova Transnistria Vojvodina European Union (See List.) |
|
Recognised minority
language in |
Hungary
Serbia Ukraine |
| Regulated by |
Academia Română Academy of Sciences of Moldova |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | ro |
| ISO 639-2 |
rum (B)ron (T)
|
| ISO 639-3 | |
| Glottolog | roma1327 |
| Linguasphere | 51-AAD-c (varieties: 51-AAD-ca to -ck) |

Blue: region where Romanian is the dominant language. Green: areas with a notable minority of Romanian speakers.
|
|
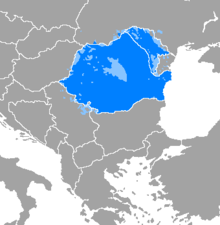
Distribution of the Romanian language in Romania, Moldova and surroundings.
|
|
Romanian (obsolete spellings Rumanian, Roumanian; autonym: limba română [ˈlimba roˈmɨnə], "the Romanian language", or românește, lit. "in Romanian") is a Romance language spoken by around 24-26 million people as a native language, primarily in Romania and Moldova, and by another 4 million people as a second language. It has official status in Romania and the Republic of Moldova. It is one of the official languages of the European Union.
Romanian is a part of the Balkan-Romance group that evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin separated from the Western Romance during the 5th–8th centuries. To distinguish it within that group in comparative linguistics it is called Daco-Romanian as opposed to its closest relatives, Aromanian, Megleno-Romanian, and Istro-Romanian.
During Soviet times—and to some extent even today—Romanian was called Moldovan in the Republic of Moldova, although the Constitutional Court ruled in 2013 that "the official language of the republic is Romanian".
Romanian speakers are scattered across many other countries, notably Australia, Italy, Spain, Ukraine, Bulgaria, the United States, Canada, Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, Greece, Turkey, Russia, Portugal, the United Kingdom, Cyprus, France and Germany.
Eastern Romance languages, like the other branches of Romance languages, descend from Vulgar Latin, adopted in Dacia by a process of Romanization during early centuries AD.
...
Wikipedia
