Rift Valley, Kenya

Lake Bogoria, one of the main lakes in the Great Rift Valley.
|
|
| UNESCO World Heritage Site | |
|---|---|
| Official name | Lake Bogoria, Great Rift Valley, Kenya |
| Location | Kenya |
| Coordinates | 00°26′33″N 36°14′24″E / 0.44250°N 36.24000°ECoordinates: 00°26′33″N 36°14′24″E / 0.44250°N 36.24000°E |
| Area | 32,034 ha (3.4481×109 sq ft) |
| Includes |
Cherangany Hills Lake Baringo Lake Bogoria Lake Elmenteita Lake Logipi Lake Magadi Lake Naivasha Lake Nakuru Lake Turkana |
| Criteria | Natural: Natural: (vii)(ix)(x) |
| Reference | 1060 |
| Inscription | 2011 (35th Session) |
|
[]
|
|
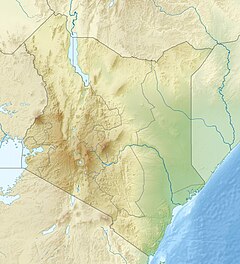
The Great Rift Valley is part of an intra-continental ridge system that runs through Kenya from north to south. It is part of the Gregory Rift, the eastern branch of the East African Rift, which starts in Tanzania to the south and continues northward into Ethiopia. It was formed on the "Kenyan Dome" a geographical upwelling created by the interactions of three major tectonics: the Arabian, Nubian, and Somalian plates. In the past, it was seen as part of a "Great Rift Valley" that ran from Madagascar to Syria. Most of the valley falls within the former Rift Valley Province.
The valley contains the Cherangani Hills and a chain of volcanoes, some of which are still active. The climate is mild, with temperatures usually below 28 °C (82 °F). Most rain falls during the March–June and October–November periods. The Tugen Hills to the west of Lake Baringo contain fossils preserved in lava flows from the period 14 to 4 million years ago. The relics of many hominids, ancestors of humans, were found here.
The valley is bordered by escarpments to the east and west. The floor is broken by volcanoes, some still active, and contains a series of lakes. Some of the soils are Andisols, fertile soils from relatively recent volcanic activity.
Lake Turkana occupies the northern end of the Great Rift Valley in Kenya. There are also volcanoes in Lake Turkana. The Suguta Valley, or Suguta Mud Flats, is an arid part of the Great Rift Valley directly south of Lake Turkana. The shield volcano Emuruangogolak straddles the valley to the south of Suguta, and further south Mount Silali and Paka rise from the valley floor. Paka is a shield volcano, with widespread geothermal activity. South of Paka are Mount Korosi, Lake Baringo and Lake Bogoria. Menengai is a massive shield volcano in the floor of the rift with a caldera that formed about 8,000 years ago. It overlooks Lake Nakuru to the south. This region also includes Lake Elementaita, Mount Kipipiri and Lake Naivasha.
...
Wikipedia