Ribavirin
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | RYE-ba-VYE-rin |
| Trade names | Copegus, Rebetol, Virazole, other |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a605018 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
by mouth, solution for inhalation |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 64% |
| Protein binding | 0% |
| Metabolism | liver and intracellularly |
| Biological half-life | 298 hours (multiple dose); 43.6 hours (single dose) |
| Excretion | Urine (61%), faeces (12%) |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
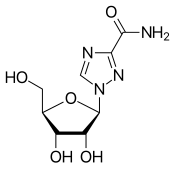
| Synonyms | 1-(β-D-Ribofuranosyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| NIAID ChemDB | |
| PDB ligand | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.164.587 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C8H12N4O5 |
| Molar mass | 244.206 |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Ribavirin, also known as tribavirin, is an anti-viral medication used to treat RSV infection, hepatitis C, and viral hemorrhagic fever. For hepatitis C it is used with other medications such as simeprevir, sofosbuvir, peginterferon alfa-2b or peginterferon alfa-2a. Among the viral hemorrhagic fevers it is used for Lassa fever, Crimean–Congo hemorrhagic fever, and Hantavirus infection but not Ebola or Marburg. Ribavirin is taken by mouth or inhaled.
Common side effects include feeling tired, headache, nausea, fever, muscle pains, and an irritable mood. Serious side effects include red blood cell breakdown, liver problems, and allergic reactions. Use during pregnancy results in harm to the baby. Effective birth control is recommended for both males and females for 7 months after use. The mechanism of action of ribavirin is not entirely clear.
Ribavirin was patented in 1971 and approved for medical use in 1986. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system. It is available as a generic medication. In the United States a course of treatment costs more than 200 USD.
...
Wikipedia
