Rhenium heptoxide
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Rhenium heptoxide
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.857 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| Re2O7 | |
| Molar mass | 484.40298 g/mol |
| Appearance | yellow crystalline powder |
| Density | 6.103 g/cm3, solid |
| Melting point | 360 °C (680 °F; 633 K) |
| Boiling point | sublimes |
| Hazards | |
|
EU classification (DSD) (outdated)
|
not listed |
| Related compounds | |
|
Related compounds
|
Manganese(VII) oxide; technetium(VII) oxide; perrhenic acid |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Rhenium(VII) oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Re2O7. This yellowish solid is the anhydride of HOReO3. Perrhenic acid, Re2O7·2H2O, is closely related to Re2O7. Re2O7 is the raw material for all rhenium compounds, being the volatile fraction obtained upon roasting the host ore.
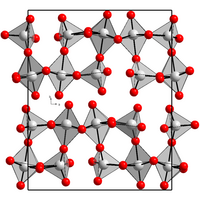
Crystalline Re2O7 is an inorganic polymer, which consists of alternating octahedral and tetrahedral Re centres. Upon heating, the polymer cracks to give molecular (nonpolymeric) Re2O7. This molecular species closely resembles manganese heptoxide, consisting of a pair of ReO4 tetrahedra that share a vertex, i.e., O3Re-O-ReO3.
Rhenium(VII) oxide is formed when metallic rhenium or its oxides or sulfides are oxidized at 500-700 °C in air.:
Re2O7 is very reactive toward water. It dissolves in water to give perrhenic acid. It is a precursor to methylrhenium trioxide ("MTO"), a catalyst for oxidations.
Rhenium(VII) oxide finds some use in organic synthesis as a catalyst for carbonyl reduction and amide reduction.
...
Wikipedia
