Rail transport in Thailand
| Rail transport in Thailand | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||
| Operation | |||||
| National railway | SRT | ||||
| Infrastructure company | SRT | ||||
| Major operators | BTSC, BMCL | ||||
| Statistics | |||||
| Ridership | ? | ||||
| System length | |||||
| Total | 4,346 kilometres (2,700 mi) | ||||
| Electrified | 80.55 km (50.05 mi) (rapid transit) | ||||
| High-speed | 0 km (0 mi) | ||||
| Track gauge | |||||
| Main |
1,000 mm (3 ft 3 3⁄8 in) 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) |
||||
| Metre gauge | 4,346 kilometres (2,700 mi) | ||||
| Standard gauge | 80.55 km (50.05 mi) (rapid transit) | ||||
| Electrification | |||||
| Third rail | 51.95 km (32.28 mi) (BTS Skytrain and MRT (Bangkok)) | ||||
| Overhead line | 28.6 km (17.8 mi) (Suvarnabhumi Airport Link) | ||||
| Features | |||||
| No. tunnels | 7 | ||||
| Tunnel length | 3.626 km (2.253 mi) | ||||
| Longest tunnel | 1.352 km (0.840 mi) (Khun Tan Tunnel) | ||||
| Longest bridge | 0.442 km (0.275 mi) (Rama VI Bridge) | ||||
| Highest elevation | 578m (Khun Tan Railway Station) | ||||
|
|||||
| Map | |
|---|---|
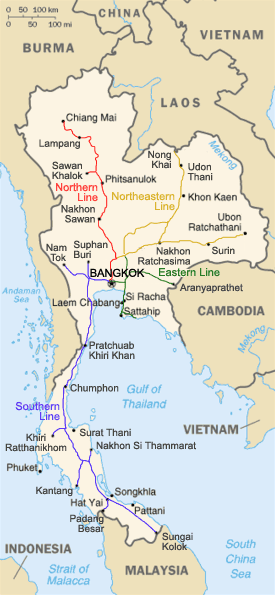 |
| Thailand high-speed rail | |
|---|---|
| Overview | |
| Type | High-speed rail |
| Status | Preliminary |
| Operation | |
| Operator(s) | State Railway of Thailand |
| Technical | |
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) |
| Operating speed | 250 km/h (155 mph) max |
The railway network of Thailand is managed and operated by the State Railway of Thailand (SRT).
Interest in rail transport in Siam can be traced to when King Rama IV was given a gift of a model railway from Queen Victoria in 1855. The first railway line, 20 km in length, named the Paknam Railway between Bangkok–Samut Prakan began construction in July 1891 under a 50-year concession with a Danish company. Paknam Railway opened in 1894. This railway line was electrified in 1925, made it into the first electric railway service of Southeast Asia. This railway line was decommissioned on 1 January 1957.
Royal State Railways of Siam (RSR) was found in 1890 at the same time with a construction of the Bangkok-Ayutthaya railway (71 km or 44 mi), the first part of the Northern Line, was started in 1891 and opened on 26 March 1895. The Thonburi-Phetchaburi line (150 km or 93 mi), later the Southern Line, opened on 19 June 1903.
The Northern Line was originally built as 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) standard gauge, but in September 1919 it was decided to standardize on 1,000 mm (3 ft 3 3⁄8 in) metre gauge and the Northern Line was regauged during the next ten years. On 1 July 1951, RSR changed its name to the present State Railway of Thailand (SRT).
In 2005 SRT had 4,070 km (2,530 mi) of track, all of it metre gauge. Nearly all is single-track, although some important sections around Bangkok are double or triple-tracked and there are plans to extend this.
On 21 March 2015 Prime Minister Gen Prayut Chan-o-cha said that Thailand and China had signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) in late-2014 on joint railway construction furthering Thailand's seven-year strategy on the development of transportation from 2015-2022. The MoU stipulates that a joint Thai-Chinese 1.435 metre standard-gauge rail network project bear fruit in 2018. Thailand is to be responsible for conducting environmental impact assessments and land expropriations. China is responsible for project design and construction. The project includes four routes: 133 km between Bangkok and Kaeng Khoi; 246.5 km between Kaeng Khoi and Map Ta Phut; 138.5 km between Kaeng Khoi and Nakhon Ratchasima; and 355 km from Nakhon Ratchasima to Nong Khai.
...
Wikipedia
