Polyaspartic acid
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
PASP
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| 25608-40-6 (poly-L-aspartic acid) | |
| Properties | |
| (C4H5NO3)n | |
| Molar mass | variable |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Polyaspartic acid (PASA) is a biodegradable, water-soluble polyaminoacid. It is discussed as a possible replacement of many non-biodegradable polymers. It is used as a homopolymer and in various copolymers. In nature, PASA has been found in as fragments of larger proteins with length up to 50 amino acids, but as of 2004 had not been isolated as a pure homo polymeric material from any natural source. The first isolation of synthetic oligomeric sodium polyaspartate, obtained by thermal polycondensation of aspartic acid, was reported by Hugo Schiff in late 19th century. Later it was proposed that thermal polymerization process leads through polysuccinimide intermediate. Polyaspartic acid is produced industrially in both the acid form and as the sodium polyaspartate salt.
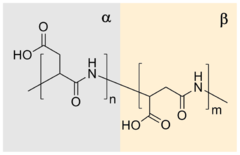
Due to presence of carboxylic groups it is polyelectrolyte with anionic character. Naturally occurring PASA fragments consists of α,-linked L-aspartatic acid. In contrast, the repeating unit of synthetic polyaspartic acid may exist in four isomeric forms, depending on the stereochemistry of starting material (D- and L-aspartic acid) and synthetic procedure leading to α and β links.
Many different routes lead to PASA. In the simplest and the oldest approach aspartic acid is heated to induce dehydration. In a subsequent step the resulting polysuccinimide is treated with aqueous sodium hydroxide, which yields partial opening of the succinimide rings. In this process sodium-DL-(α,β)-poly(aspartate) with 30% α-linkages and 70% β-linkages randomly distributed along the polymer chain, and racemized chiral center of aspartic acid is produced. There were many catalysts reported for improving thermal polymerization method. Main benefits from their application is increasing of the conversion rate and higher molecular weight of the product. Polyaspartic acid can also be synthesized by polymerization of maleic anhydride in presence of ammonium hydroxide. High control over repeating unit isomers can be achieved by polymerization of N-carboxyanhydride (NCA) derivatives, by polymerization of aspartic acid esters or by application of enzyme catalyzed reaction. Pure homopolymers, D- or L-PASA with α- or β-links only, can be synthesized using those methods.
...
Wikipedia
