Pinus kesiya
| Pinus kesiya | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Pinophyta |
| Class: | Pinopsida |
| Order: | Pinales |
| Family: | Pinaceae |
| Genus: | Pinus |
| Subgenus: | Pinus |
| Species: | P. kesiya |
| Binomial name | |
|
Pinus kesiya Royle ex Gordon |
|
Pinus kesiya (Khasi pine, Benguet pine or three-needled pine) is one of the most widely distributed pines in Asia. Its range extends south and east from the Khasi Hills in the northeast Indian state of Meghalaya, to northern Thailand, Philippines, Burma, Cambodia, Laos, southernmost China, and Vietnam. It is an important plantation species elsewhere in the world, including in southern Africa and South America.
The common name "Khasi pine" is from the Khasi hills in India, and "Benguet pine" is from the landlocked province of Benguet in Luzon, Philippines, where it is the dominant species of the Luzon tropical pine forests. The Benguet pine is sometimes treated as a separate species, Pinus insularis; however, the current opinion is to treat these as conspecific with P. kesiya. The city of Baguio is nicknamed "The City of Pines", as it is noted for large stands of this tree.
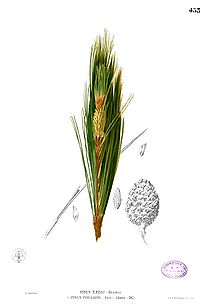
Pinus kesiya is a tree reaching up to 30–35 m tall with a straight, cylindrical trunk. The bark is thick and dark brown, with deep longitudinal fissures. The branches are robust, red brown from the second year, the branchlets horizontal to drooping. The leaves are needle-like, dark green, usually 3 per fascicle, 15–20 cm long, the fascicle sheath 1–2 cm long and persistent. The cones are ovoid, 5–9 cm long, often curved downwards, sometimes slightly distorted; the scales of second-year cones are dense, the umbo a little convex, sometimes acutely spinous. The scales have transverse and longitudinal ridges across the middle of the scale surface. The seeds are winged, 6–7 mm long with a 1.5-2.5 cm wing. Pollination is in mid spring, with the cones maturing 18–20 months after.
...
Wikipedia

